
▶ Previous Artlcle: Combination Treatment with Long-pulsed 755‧1064 Laser and Pico 1064‧532 Laser Ⅲ
Effective Approach Based on Correct Determination of Pigments
Before listening to my personal method for pigment treatments, it may be helpful for you to understand nevus first for better results. Nevus has three meanings: Firstly, it means congenital pigmentation or pigmentation that occurs in childhood. In addition, Ota nevus has the meaning of melanocytes benign tumor which we usually think of. Finally, It is the junctional nevus which has the meaning of hamartoma. The black portion of the hair or sebaceous glands is sometimes called nevus, which refers to hamartoma.
Personally, I first look at the spots first when it comes to the method for differentiating the pigments. I check the spots to determine their types among the compound nevus, junctional nevus, intradermal nevus, and congenital melanocytic nevus. Secondly, I check the epidermal pigmentation. I check the spots to see if they are freckles, lentigines or melasmas. Finally, I check the abnom in dermis. If you look into those spots, you will be able to determine 99% of the pigments. You will feel confused if you think about other methods at the same time.
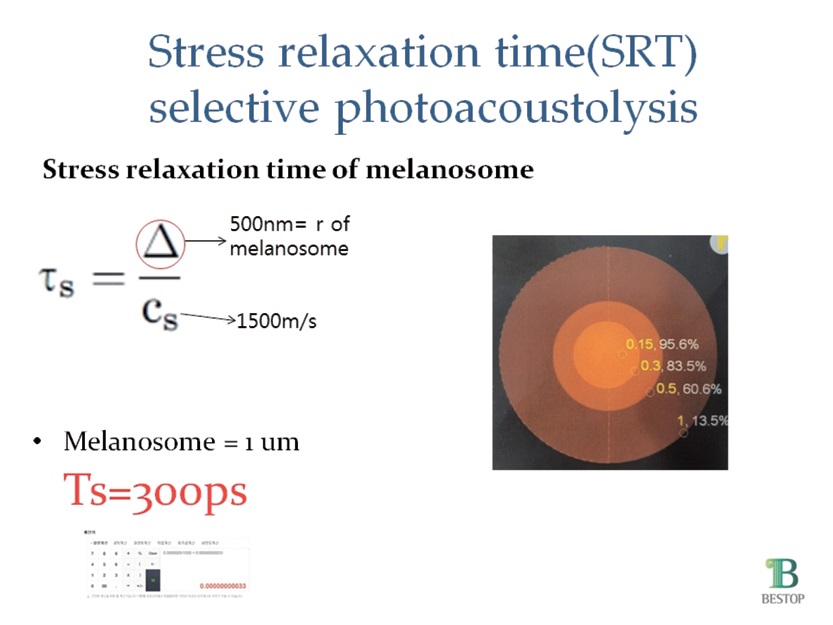
Fig. 2. Stress Relaxation Time applied to lesion.
[Advertisement] PICOCARE - Manufacturer: WONTECH(www.wtlaser.com)]
The nevomelanocyte accumulated only in the confines of epidermis is called junctional nevus, while nevomelanocyte accumulated into dermis is called compound nevus. The intradermal nevus refers to the nervus gathered only in the confines of dermis while approaching the epidermis. It is easy to distinguish between junctional nevus and compound nevus. Junctional nevus can be burned with a long-pulsed laser, cut with an Er:YAG laser, or broken with a Q-switched laser. Compound is different. As the compound has nevomelanocytes deep into the epidermis, ablation is needed or long-pulsed lasers should be irradiated several times.
Spots recur even if they are cut with CO₂ Laser or Er: YAG Laser to an extent that they are almost invisible. Nevomelanocytes remain. That is because there are residual Nevomelanocytes. The residual nevomelanocytes do not have melanin and therefore do not look black. The residual nevomelanocytes look black again as they come close to the epidermis later and begin to produce melanin by receiving the signals from cytokines or hormones, etc., from keratinocytes. So, spots to be pulled out have to be cut deeply. When the spots get upward, they just need to be cut again. And it is the intradermal nevus. I was very confused as to why it was called a ‘spot’. The epidermis is usually normal with large nevomelanocytes present deep in the dermis. The texture looks clean. It just needs to be cut several times.
-To be continued




















