▶ Previous Artlcle: #12-3. Fractional Laser
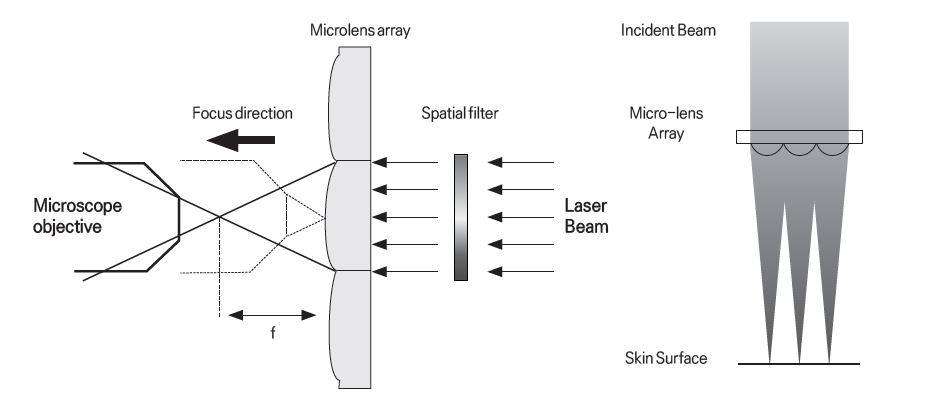
For the DOE type, the bulk beam passes through diffractive option element and generates a multi-micro spot after the fractional beam passes through focus lens, which makes it easier to adjust the size and number of the beam as desired.
And, no significant difference in terms of energy between the center and the edge is present, because the same amount of energy can be delivered to each spot.
However, due to the shorter beam waist compared to the MLA type, any change in the tip-skin distance during the procedure may cause the beam to be out of focus.
That is why, despite the high single microbeam fluence compared to the MLA type, only a little energy exists actually working in the dermis because most of the energy is lost in the keratin layer of the dermis.
What’s more, lots of unnoticeable and invalid little beams are created in the surrounding areas, leading to about 15% of the bulk beam energy loss.
[Advertisement] PICOCARE - Manufacturer: WONTECH(www.wtlaser.com)]
The scanner type is mainly applied to CO2 Fractional Laser, Er:Glass fractional laser, and thulium fractional laser.
Its small bulk beam spot size can produce the desired density and range of fractional beams according to the angle of refraction of the two reflecting mirrors inside the scanner when a microbeam with a diameter of 100 to 200 µm passes through the scanner.
Fractional Laser has a variety of treatment purposes including photorejuvenation, melasma, acne scar, large pore, striaedistensae, hypopigmented surgical scar, hyperpigmentation, telangectasia, residual hemangioma, and fine wrinkle.
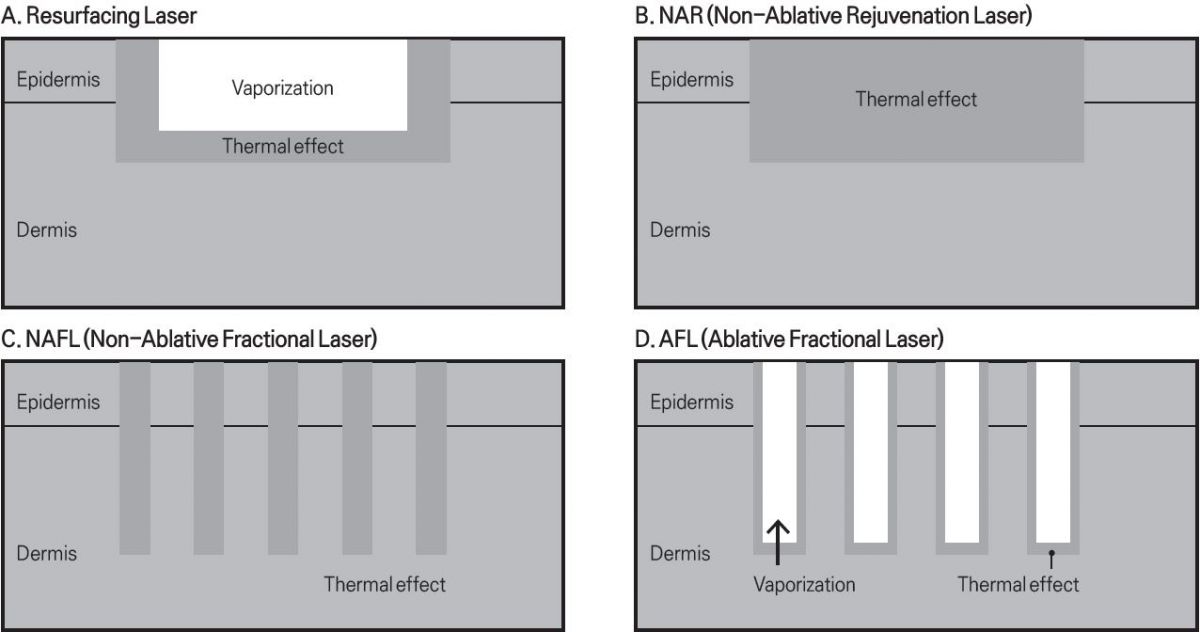
Picture 3. Laser tissue interaction.
Picture 4. Fractional Laser beam (MLA).
-To be continued