Resveratrol
Resveratrol is a type of stilbene and is found in various plants such as mulberries, peanuts, grapes, raspberries, and cranberries, etc. Grapes release resveratrol as a defense mechanism against fungus. Resveratrol lowers serum cholesterol, has anti-cancer, antioxidative, antiviral, neuro-protective, anti-inflammatory, and anti-aging effects as well as protects against diabetes.
French paradox refers to the phenomenon that the cardiovascular mortality is low in French people despite their high level of animal fat consumption. Studies have reported that long-term ingestion of red wine is related to lower cardiovascular and cancer risks. In particular, resveratrol works as a phytoalexin, antioxidant, COX inhibitor, PPAR activator, eNOS inducer, and SIRT1 activator and improves general health.
Resveratrol activates the Nrf2 pathway through intracellular endogenous antioxidant defense pathways and increases the intracellular glutathione by inducing glutamylcysteinyl ligase and glutathione peroxidase-2. Resveratrol is known to effectively prevent proliferation of cancer cells and damaged cells by modulating the expression of certain gene signal pathways involved in cellular proliferation. It was also found to inhibit release of reactive oxygen species and enhance cell survival after epidermal exposure to UVA.
Recently, 12-week topical use of resveratrol was reported to improve wrinkles, skin elasticity, pigmentation, sheen, and smoothness, etc.
[Advertisement] ULTRA THIN WALL NEEDLE – Manufacturer: AESPIO(www.aespio.com)
Glutathione
Glutathione is one of the most important antioxidants that protects the skin and brain from free radical damage. Oral intake of glutathione is not recommended as it is completely destroyed in the stomach. It is naturally generated in the human body in the forms of amino acid, glycerin, cysteine, and glutamate. Selenium, sulfur, and vitamin D are necessary ingredients of this process. Therefore, it is important to have sufficient vitamin D level through sun exposure or supplement intake. Glutathione’s large molecular weight does not allow it to infiltrate into cells but it is naturally produced in the cells. For cells to produce adequate amount of glutathione, sufficient amounts of necessary substances should be ingested through food. Studies focusing on antioxidants are examining the effect of glutathione on reducing oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. Oxidative stress has been shown to be a key pathophysiological factor in Alzheimer's disease and the brain of a patient with Alzheimer's disease has extensive oxidative damage from free radicals. Studies have also found that glutathione reduces oxidative stress that plays an important role in the progression of Alzheimer's disease.
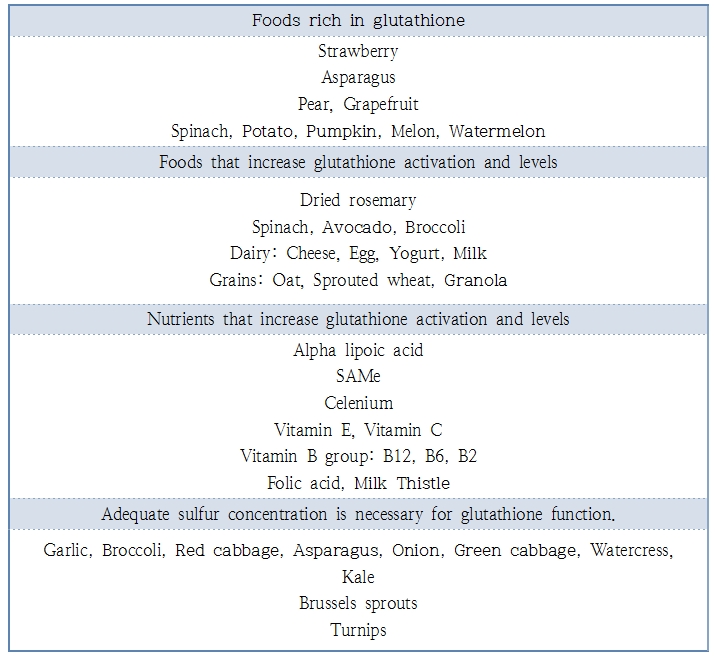
Table 1. Foods rich in glutathione.
-To be continued-