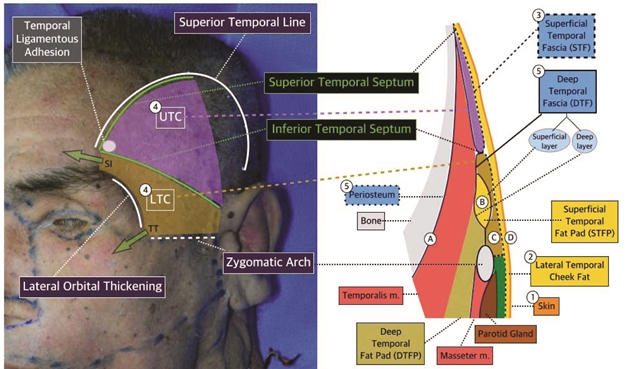
Figure 1. Anatomy of temple(TT: Temporal Tunnel, SI: Superior interval).
Anatomy of Temple
As shown in the right image in <Figure 1>, the lateral temporal cheek fat is the ⓶subcutaneous tissue under the ⓵skin of the temple and stretches to the midface. The fat in this area can be very scant and not readily distinguishable from other structures in some cases. The ⓷STF lies under the lateral temporal cheek and connects to the SMAS caudally. The STF is the first layer of mild resistance against the subcutaneously injected needle or cannula tip. The STF forms a roof over the ⓸UTC and ⓸LTC. The ⓹DTF descends from the periosteum to form the floor of the UTC and LTC. The DTF splits into the superficial layer and deep layer which surround the superficial temporal fat pad in the middle. The superficial and deep layers of the DFT joins again near the zygomatic arch. In the past, the superficial layer of the DFT was thought to attach laterally to the zygomatic arch and the deep layer attached medially to the zygomatic arch. However, Ramirez reported that the superficial and deep layers join together 1cm superior to the zygomatic arch. Moreover, Hwang et al. found that 56% of the fusion of the superficial and deep layers of the DTF attaches to the zygomatic arch’s superior margin and 44% of it attaches to the superolateral margin. They also described that the attachment between the zygomatic arch and fused DTF is within 2mm.
[Advertisement] Tulip(Skin Tightening & Lifting) – Manufacturer: DANIL SMC(www.danilsmc.com)
Superficial Temporal Fat Pad
The superficial temporal fat pad(STFP) is commonly also called the temporal fat pad(TFP). However, the deep temporal fat pad(DTFP), an extension of the buccal fat pad, lies inferior to the STFP. Therefore, the term TFP may cause confusion with this structure(Figure 1). There are many causal factors of temporal hollowing. Aging-related temporalis muscle thinning may be one or volume loss of the DTFP due to sagging and thinning of the buccal fat pad could be another. Temporal hollowing is also caused by STFP thinning. Matic et al. reported that the STFP covers 4 x 5cm of area cephalic to the zygomatic arch. Temporal hollowing is reported to deteriorate with lower Body Mass Index(BMI) related to weight loss. The STFP volume loss was also observed after surgical trauma such as incision in the area. During coronary incision, suprafacial dissection of the DTF rather than that of the superfical layer was shown to reduce temporal hollowing.
-To be continued-