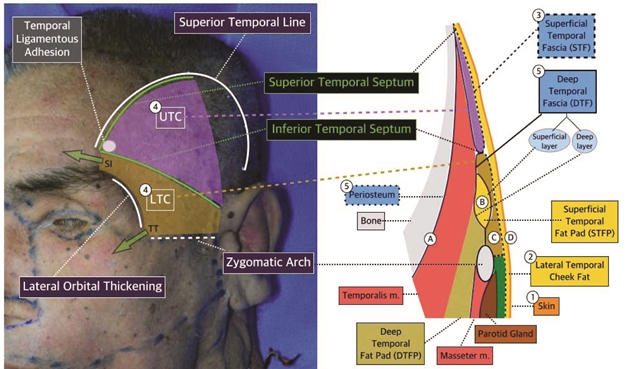
Figure 1. Anatomy of temple(TT: Temporal Tunnel, SI: Superior interval).
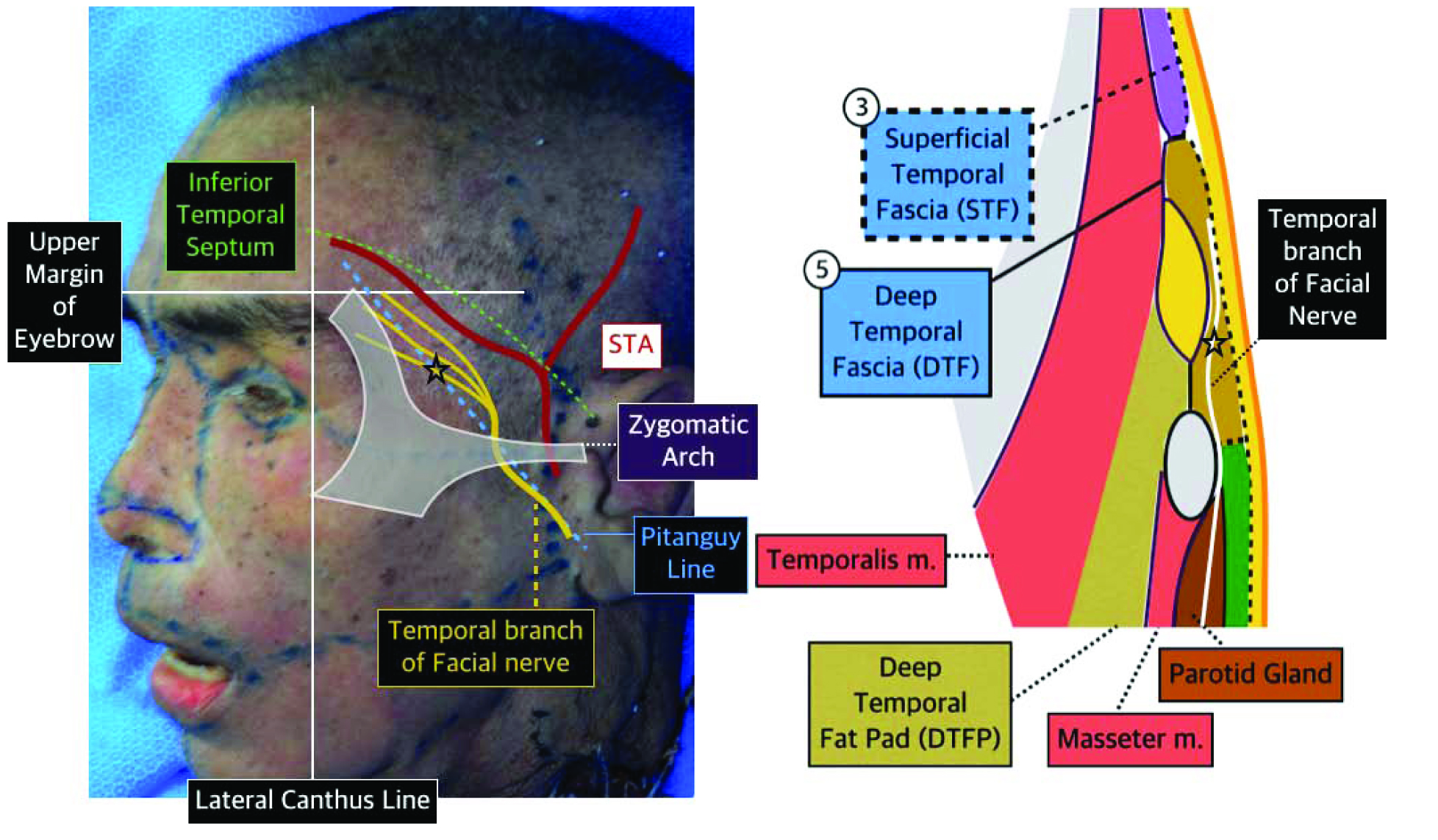
Figure 2. Position of temporal branch of facial nerve.
Upper Temporal Compartment(UTC) & Lower Temporal Compartment(LTC)
The UTC and LTC are not as extensively discussed in textbooks of anatomy. These two compartments may be thought of as spaces between layers but are also argued to be a separate layer such as fascia. The UTC is colored purple on <Figure 1> and is separated by the roof of the STF(the 3rd layer) and the floor of the DTF(the 5th layer). The STS and ITS form superior and inferior borders, respectively, and are blocked anteriorly by the hard structure of temporal ligamentous adhesion. The UTC lacks major blood vessels or nerves and is often used as a safe area to fix the anchored-type thread(Figure 1, 2).
The LTC has different characteristics from the UTC. First, whereas the UTC has a hard anterior blockage, the LTC has two anterior openings. It forms a superior interval and temporal tunnel underneath. The temporal tunnel is connected to the prezygomatic space. The second difference is that unlike the UTC that lacks fat, the LTC has more fat tissues with caudal progression. Third, the ITS at the superior border of the LTC is a blocked sheet form, whereas the LTC has no inferior border and is sparsely bordered by the zygomatic ligament. Blood vessels and nerves pass through the openings and caution is needed during surgery to avoid damaging important structures in this area(Figure 1). Moreover, the ITS is significant that it serves as a border blocking superior progression of the facial nerve temporal branch(Figure 2).
HELIOSⅡ/LOTUSⅡ/HYPERION – Manufacturer: LASEROPTEK(www.laseroptek.com)
Targeting layer of filler injection
The target layers for filler injection include Ⓐ~Ⓓ in the right image of <Figure 1>. At level Ⓐ, the filler is injected above the bone inferior to the temporalis muscle and may not show change despite a large amount of injection. However, as the tip of the needle touches the bone, this level is less susceptible to nerve or vascular damage. At level Ⓑ, the filler is injected between the superficial and deep layers of the DTF. The DTF deep layer is hard and one can feel the resistance at the tip of the cannula or needle to identify the injection depth. However, a lot of experience is required to be able to feel the deep layer after puncturing the DTF superficial layer. The risk of bleeding exists as the 5mm thick middle temporal vein passes 2cm superior to the zygomatic arch between the superficial and deep layers of the DTF. Level Ⓒ is at the LTC level and the needle comfortably reaches this level with cannula or needle injection in cadaver. Great caution is needed as the facial nerve temporal branch and superficial temporal artery pass this area. Lastly, level Ⓓ is the subcutaneous layer that lacks major nerves or blood vessels and is a safe layer for injection. However, caution is still required as uneven spread of the injected filler may result in bumpy appearance. As this layer has little subcutaneous fat, the doctor may inject in layer Ⓒ mistaking it for Ⓓ(Figure 1).
-To be continued-