8-1. Laser Types and Components
In this chapter, we will discuss about things you should know before using each type of laser. When using a car, for example, the consumables should be replaced and some parts should be cleaned on a regular basis. If left unattended, the performance of the car will be declined, even leading to major breakdown. Lasers also need consumables replaced and managed at a certain interval depending on the type. When used and managed properly according to the lifetime of consumables, lasers can maintain the best condition for as long as possible. Below are the description of laser management for 5 types of lasers:
[Advertisement] HELIOSⅡ/LOTUSⅡ/HYPERION – Manufacturer: LASEROPTEK(www.laseroptek.com)
8-1-1 Solid-state laser
There are two types of solid-state laser; Pulsed laser and Continuous Wave laser. Pulsed laser has various modes such as Q-switching (Ruby laser, Alexandrite laser, Nd:YAG laser, KTP laser, etc.), long pulse (Nd:YAG laser, Er:YAG laser) and free-running (Nd:YAG laser, Er:YAG laser). These two types use flash lamp or laser diode as the pumping source. Flash lamp generates light by electric discharge and has a certain lifetime as commonly used fluorescent or incandescent bulb. The lifetime is about several million of shots on average, although it may vary depending on the condition where the laser is used and the manufacturer.
There are few medically used solid-state laser which uses laser diode as a pumping source (for example, lower power, high repetition rates KTP laser for microvessel or high power KTP laser for prostatic hypertrophy). In this case, average 10,000 to 20,000 hours is guaranteed.
The heat generated from flash lamp or laser diode should be eliminated with cooling water. Deionized water (very pure water made by removing ions from distilled water) should be used for cooling water, but most lasers use distilled water through the attached deionized filter. Because the cooling water contained in the water tank is exposed to the air, the cooling water may be contaminated by bacterial growth. Contaminants from the cooling water adheres to pump reflector to the surface of gain medium and flash lamp, lowering laser efficiency or laser output. In order to remove contaminants, a chemical product should be used at least once a year to wash the components that have contact with the cooling water, and then the cooling water should be replaced as well.
As shown in Figure 8-1, all solid-state lasers basically have almost the same structure, and all optic components are sensitive to three factors. When managing lasers, these factors should be avoided to use the laser for a long time without a trouble.
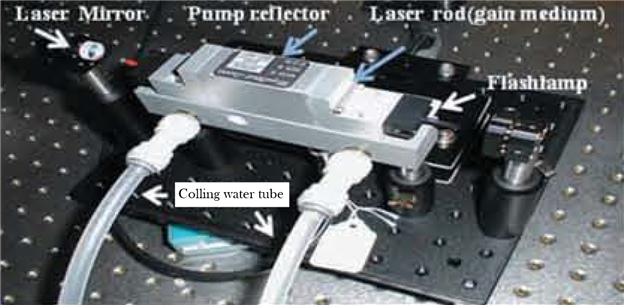
Figure 8-1. Structure of resonator in a solid-state laser
The first factor is dust. Laser light has very high energy or power per unit area compared to other light sources (high-brightness). When there is only small amount of dust on the surface of an optic component, particularly in a high power laser, the dust absorbs laser light and burns the surface, rendering the laser unable to perform its normal function. Laser should be kept in a clean room so that the laser would not be exposed to dust. This is also true when using a hand piece; any contaminants on the lens should be removed after a procedure. When contaminants are smeared on the lens of a hand piece, the dust is burned by the laser light, damaging the lens and yielding not enough energy.
The second factor is temperature. When a laser is operated in a room of high temperature (≥30℃) or without adequate ventilation, the temperature of the cooling water rises, causing physical change of the gain medium (refractive index change) and reducing the output energy or power. It is most appropriate to use laser in an air-conditioned room.
The third factor is impact. Optic components inside the resonator of a laser are aligned in a very precise manner. Severe impact or vibration from the outside may break the alignment and decrease the output or distort the shape of the beam. Any strong impact from the outside should be avoided when moving or keeping a laser.
8-1-2 Fiber laser (1540nm)
Fiber lasers have different lasing wavelength and output profiles depending on the matter used for Erbium (Er+3)-doped silica glass fiber. Laser diode (980nm) is used, in this case, for pumping source. Therefore, the only consumable of fiber laser is the pumping source.
8-1-3 Semiconductor laser/diode laser (810nm)
Recent semiconductor lasers (diode lasers) are mostly released for hair removal. When a problem occurs with regard to the diode, the diode itself should be replaced.
8-1-4 Gas laser
As the most widely used laser, gas laser includes CO2 laser and excimer laser. Gas lasers currently used for medical purpose have very simple structure where the mirror is attached, making it resistable to impacts compared to solid-state lasers. However, gas lasers use mixed gas as a gain medium and can yield the proper output when the gas is pure. Since gas laser needs electric discharge for lasing, contaminants evaporated from the electrode during electric discharge may be mixed with the gas, decreasing the purity of the gas. After using for some time, the mixed gas or pimp chamber should be replaced to a new one to obtain proper output. Excimer laser, which is commonly used for vitiligo, contains chloride, the representative element among halogens. in the mixed gas. Chloride is very active and may be fatal when exposed to human body, as much as to be used once as a poison gas during the First World War. The window that separates pump chamber and laser mirrors becomes opaque when CaF2 of the window contacts with chloride; therefore, the mixed gas as well as CaF2 window should be regularly replaced. Of course the manufacturer or the distributor will manage all these, but the user should be also well aware of these information for proper use of laser. Care should be taken, especially when using excimer laser, which uses poisonous gas.
8-1-5 Liquid laser
The most representative liquid laser is dye laser. Pulsed dye laser uses flash lamp as a pumping source, as solid-state laser, which should be replaced as mentioned earlier. Dye laser uses a solid material, called Rhodamine 6G, diluted with alcohol, as a gain medium. Since this material has a lifetime, it should be replaced to a new one when the laser output is decreased, if not regularly. Since there have been reports that Rhodamine 6G is carcinogenic, such as skin cancer, care should be taken so that the gain medium would not be smeared on the body when replacing it.
- To be continued-
▶ Previous Artlcle : #5. Types and Characteristics of Lasers for Skin Treatment
▶ Previous Artlcle : #7. Factors to be considered before Purchasing Dermatologic Lasers