▶ Previous Artlcle : #5-2. Understanding IPL
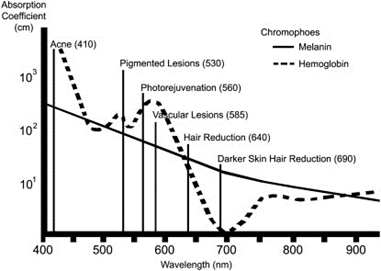
Figure 1. Absorption coefficient of chromophores in various wavelengths and wavelengths selected for clinical indications
Advantages and disadvantages of IPL
Compared to other devices, IPL has unique advantages and disadvantages. Its key advantage would be the wide range of indications. IPL can simultaneously address pigment, erythema, vascular dilation and hair removal. The recently released pulse-in-pulse type IPL shows moderate efficacy in melasma treatment. Due to its wide application, IPL is the most favored device in private practices with limited budget.
Another key advantage is the affordability of the device. Photomedical devices easily cost over KRW 100 million (about USD 100,000), but IPL devices are available at a portion of this cost, lowering the financial burden of the clinician. The large spot size allows shorter treatment time. The IPL device is stable and malfunction is rare.
[Advertisement] ATLAS(Long pulse 532nm & 940nm dual wavelength) – Manufacturer: MEDRO(www.medro.net)
A disadvantage of IPL, on the other hand, would be the fluence reduction with use. The user should regularly check for lowered fluence. The handpiece is equipped with cooling water and therefore is heavy and bulky. Necessary use of cooling gel during procedure is another disadvantage. The large spot size can also be a disadvantage. As mentioned above, it is useful for shortening treatment time, but meticulous treatment of small lesions may cause side effects as surrounding healthy tissues are also irradiated.
I have covered merits and demerits of IPL, but personally I believe IPL’s advantages outweigh disadvantages.
Considerations for clinical use
Accurate selection of patients is very important for IPL treatment. The doctor should develop skills to accurately identify lesions best treated by IPL. During my trainee years, the biggest challenge with IPL treatment was no response or darkening of pigment lesions in patients with unclear complexions.
In general, IPL more effectively removes epidermal pigments rather than deeper dermal lesions. In other words, dark brown lesions with clear boundaries are most suitable for IPL. Light brown or grayish brown lesions with blurred edges are unlikely to respond to treatment. IPL may lighten the coloration of moles, but cannot alone completely remove them. Novice users who have difficulty locating pigment lesions should resort to Wood’s lamp test or UV images prior to IPL treatment to more accurately measure the depth of the target lesion.
During IPL procedure, particular attention should be paid to the area under the lateral corner of the eye. Very subtle epidermal melisma (VSEM) undetected by gross examination exists in this area. Ignoring VSEM could cause newly developed hyperpigmented lesions in this area. Melasma formed this way does not respond to various treatments and can pose a serious problem to the doctor. Wood’s lamp or UV images can help check for existence of VSEM.
The patient should be sufficiently informed of complications associated with IPL. As patients tend to forget doctor’s warnings or explanations, verbal communication can be supplemented by written instructions. As lawsuits on aesthetic medicine malpractice are increasing, a doctor should prepare a written consent form for the patient to sign prior to treatment. The information sheet should explain common post-procedure side effects such as blisters, crust, erythema, hyperpigmentation, hypopigmented spots, and scars.
-To be continued-
▶ Next Artlcle : #6-2. Considerations for clinical application