The intense pulsed light (IPL) comprises a broad spectrum of light waves (500–1,200 nm) emitted non-coherent light that allows variations in pulse length, mode, delay between pulses, and fluence. By varying combinations of wavelengths, pulse durations, pulse intervals, and fluences, IPLs have been employed for the treatment of a broad range of skin disorders, such as photodamaged skin, pigmented lesions, vascular lesions, acne vulgaris, unwanted hair growth, scars, and angiokeratoma etc.
Clinical effects of IPL on photoaged skin have revealed clinical improvement of wrinkles, dyspigmentation, and telangiectasias. The microscopic findings revealed degrees of collagen formation, elastic fiber proliferation, reduced dermal inflammation, and improvement of solar elastosis. Selective and mild thermal damage of dermal collagen leading to coagulative degeneration and subsequent reactive synthesis of neocollagens without damaging the epidermis is the most widely proposed mechanism for its effects on rejuvenation.
.jpg)
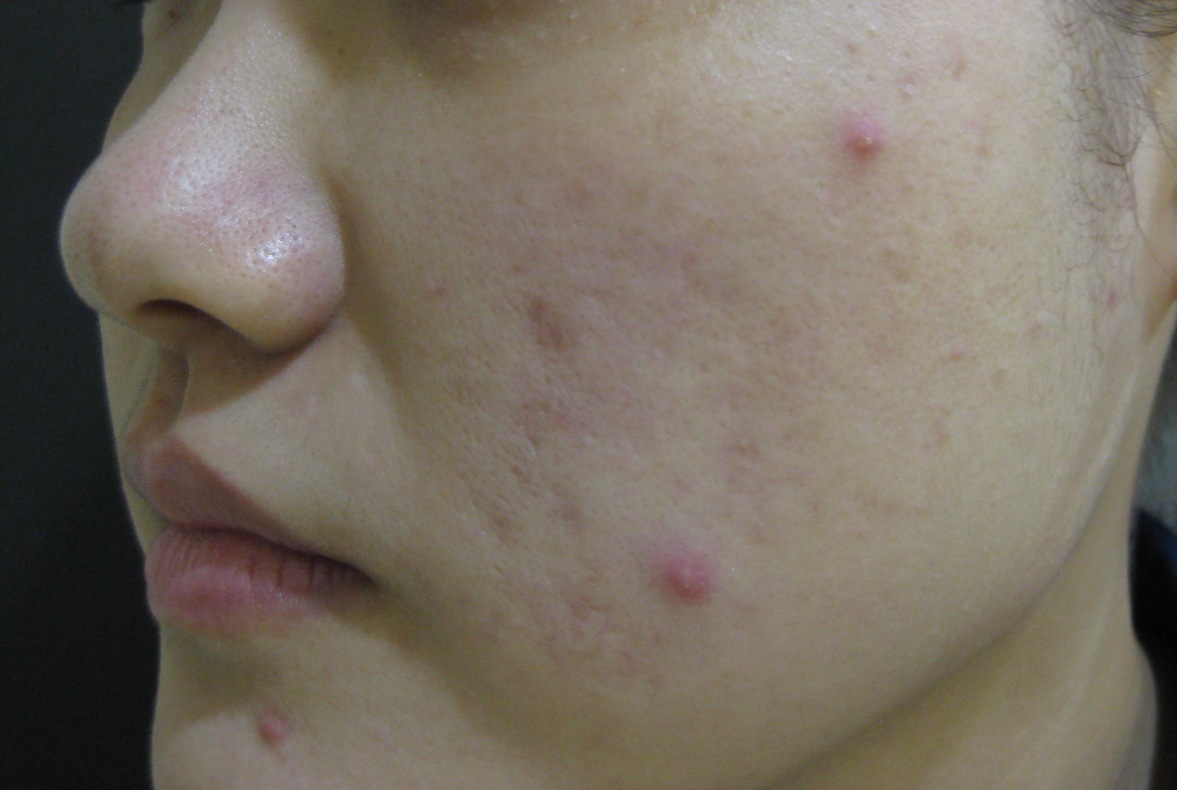
Figure1a and b: Before and after one session of IPL for acne and pore size . (Courtesy of Dr. Hsuan-Hsiang Chen)
It has also been used to treat pigmented lesions with promising results in recent years. Regarding wavelengths, IPL sources can be used with lower cutoff filters to treat superficial pigmentation, such as freckles, and higher cutoff filters for deeper lesions, such as nevus spilus. Superficial pigmented lesions respond better than deeper lesions. The lack of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) is the overwhelming advantage of IPL. However, multiple treatment sessions are required to achieve excellent clearance.
[Advertisement] FCR® (Fractional Prickle CoralCalcium Regentron) – Manufacturer: (www.illglobal.com)]
Although IPL technology has been popularly employed in clinical treatments for dermatological and cosmetic purposes in recent years, the underlying mechanisms of its functions are not fully elucidated. Recently, the possibility that one of the functional mechanisms of IPL might be related to the regulation of aquaporin protein expression was noted. We will introduce the whole spectrum of IPL from basic research to its clinical applications.
-To be continued