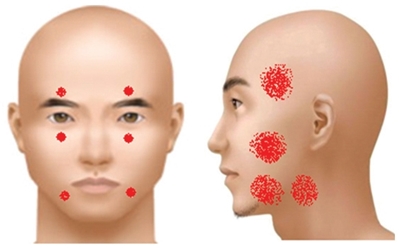
Image. Facial danger zones(front and side).
4. Nerve damage
Facial areas susceptible to motor nerve damage are called ‘danger zones’. As seen below, there are 14 danger zones; 6 on the front and 8 on both sides of the face.
The anatomical knowledge required for preventing facial nerve damage and major clinical manifestations of nerve damage are as following.
① Damage of nerves that lie along the lines through the center of pupil can occur in dermatologic surgery procedures. Supratrochlear nerve damage can occur during corrugator muscle dissection in forehead lift. The risk of supraorbital nerve damage rises with subperiosteal forehead lift using endoscope. Blind dissection beyond 2cm from the supraorbital margin should be avoided to prevent nerve injury. Infraorbital nerve also lies on the subperiosteal plane. Mental nerve should also be protected during subperiosteal approach in the mandible.
② Damage of the facial nerve’s temporal branch that frequently occurs after removal of invasive basal cell carcinoma in the temple causes eyebrow and eyelid ptosis as well as severe forehead muscle paralysis. This nerve courses within the temporoparietal/SMAS fascia. Therefore, dissection above this layer (subcutaneous) or lower at subtemporoparietal/sub-SMAS level can avoid nerve damage.
③ Zygomatic branches innervate the zygomaticus major and is less likely to be damaged but sub-SMAS dissection carries a high risk of nerve damage.
④ Buccal branch is in danger during sub-SMAS dissection. If paralysis occurs, the ipsilateral mouth corner droops causing difficulty in eating and an asymmetrical smile.
⑤ The marginal mandibular branch is rarely visible during the facial lift and contouring procedure. The safest approach would be sub-SMAS dissection. It courses behind blood vessels in the mandible and caution is needed for hemostasis. When this nerve is damaged, the ipsilateral mouth corner does not go up, resulting in an asymmetrical smile. Moreover, the patient with this nerve damage cannot make creases in the chin and suffers speaking problems as there is difficulty pronouncing g, p, and q.
[Advertisement] Selene(Diode hair removal Laser) – Manufacturer: (www.senbitec.com)]
5. Suture reactions
Suture reactions occur more frequently with use of buried materials such as suture thread, and collagen foam, etc.
Suture reactions occur in a few weeks to a month after surgery. The basic treatment involves injection on the site of lesion (triamcinolone 10mg/ml) with or without foreign body removal. When possible, the wound can be reopened. In this case, suture threads different from the previous suture should be used. Hemorrhagic granuloma can occur with use of anticoagulant or presence of coagulopathy and can be treated with incision, drainage and antibiotic therapy.
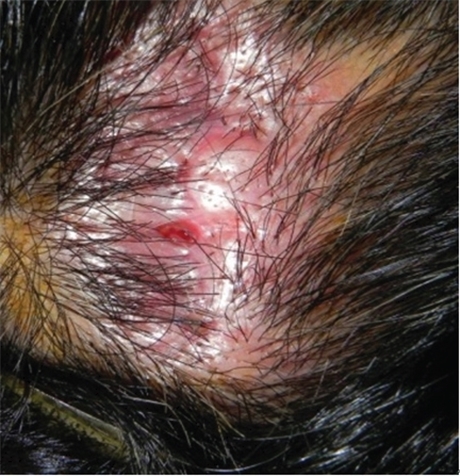
Image 1. Suture reaction after nevus sebaceous excision of the scalp.
-To be continued-





















