Pre-surgical procedures for performance of the Skin tumorectomy
Informations that should be included in the patient information sheet and the informed consent
• Bleeding, infection, scar, injury of fringe tissues and recurrence.
• Potential risks and detailed complication.
• Documented data
• All of surgical procedures possible practicable before the day of surgery.
• Questions and inquiries.
• Describe what the patient wants.
[Advertisement] COPPER BROMID(Yellow/Green Laser) – Manufacturer: BISON(www.bisonmedical.com)
Preparation before performing the procedures of skin tumorectomy
• Detailed physical examination (in preparation for potential complications).
1. Range of resectable lesion.
2. Histologic definitive diagnosis.
3. Recording the risk of metastasis and the examination of pre-resection lymph node.
4. Expected size of defect area.
• Provision of sufficient information to patients.
• Establishment of surgical plan in prior to start the surgery.
• Identification of past history.
1. Risk of stimulation by electrocauteries including artificial pacemaker, defibrillator and etc.
a. Battery type cautery is safe but inaccurate.
b. Bipolar forceps are excellent alternative but difficult to use for electrocoagulation/curettage.
c. Standard cautery (without earthing) is hazardous.
d. The hazard gets reduced as being distant from the equipment further away (thoracic wall vs. nail plate .
e. Short procedures time with lower energy as possible.
f. Hemostasis to be conducted by tieing the bleeding part as possible.
g. Consider the heart rate monitoring.
h. Some devices are unrelated with magnetics(Consider pre-surgical collaborative practice with the department of circulatory internal medicine.
* Smokes to be generated from performing the procedures of electro-cautery
Lung injury, carcinogens and mutagenic substances. Papilloma and herpes virus are identified. HIV is still uncertain and the hepatitis virus is not studied.
2. Antithrombotics: Should it be discontinued before the surgery.
a. Warfarin: Even if continually taken, the risk of complications is minimal. If discontinued, the risk of thromboembolism will be in the range of 4~58%.
b. Aspirin: Even if continually taken, the risk of complications is minimal. The risk of thromboembolism is not identified when discontinued.
c. Recommendations.
A. Do not discontinue the medications prescribed from other clinical department arbitrarily without collaborative consultation with the concerned department .
B. Continue to administrate all the medications required and take cautions for in-surgery hemostasis.
C. Post-surgical use of ice, compression and education.
D. Any antithrombotics being administered as required should be discontinued (Aspirin: 2 weeks in prior, NSAIDS, Vitamin E, Korean Traditional Medicines-Red Ginseng, Ginkgo biloba Extract and etc: at least 2~3 days in prior).
3. Actual allergic reaction to the local anesthetic agent is rare but common than we think.
a. There is no cross-reaction between amides(lidocaine) and esters(procaine).
b. Actual allergic reaction should be differentiated with needle phobia and epinephrine-induced tachycardia.
c. Preservatives-free lidocaine: No PABA(para-Aminobenzoic acid) or bisulfite-inducer.
d. Definite diagnosis to be made by skin test.
e. Perspiration, tachycardia, hypotension, stridor: Epinephrine subcutaneous injection.
f. Alternatives when it is impossible to use Amide/Ester anesthetics.
1. Local Cooling: Anesthetic effects are obtained by using a vapocoolant spray containing liquid nitrogen repeatedly. For a few seconds.
2. Anti-microbial saline solution: Anesthetic effects are obtained by local injection. For 1~2 minutes.
3. Diphenhydramine: Injection of diluted 1% solution, sedative effects.
4. Anxiety control: Enjoyable conversation with patients, use of humors, etc.
Prevention of Surgery-Related Safety Accident
Preparation of protective gears against sharp instrument, routine training, especially for handling of syringe needle
• Vaccination for Hepatitis prevention is essential because of contact with body fluids such as blood.
• Thorough disinfection of tools and the operation room.
• Habituation of glove use.
Thorough disposal of medical wastes
• Prepare the surgical tool set by usage -Use a tray for preparation in advance(Figure 1&2).
• Use the right tools by region and by treatment.
e.g.) Eye shield, Chalazion clamp(Figure 3), Microsurgery set, and Loope.
Significant prior knowledge required for prevention of local anesthesia-related complications
Use of epinephrine together with anesthetic agent
• Most of local anesthesia uses a diluted 1% solution of lidocaine for dental use (2%, 1:100,000 Epinephrine) but it is safe not to use it on penis or fingers.
Methods considerable to reduce the pain of anesthesia
1. The pain can be reduced by using a small syringe in the size of 30G, spreading anesthetic agent on the skin before injection of the anesthetics, or by spraying the coolant. While injecting the anesthetic agent, rub the skin (pinch method).
2. Regional blocking anesthesia(nerve block; useful for anesthesia of nose or ear).
3. As possible, use one hole and inject the anesthetic to crepuscular direction.
4. Injection rate- Inject it as slow as possible.
5. The acid level of lidocaine is in the range of pH 6.6-6.8 but epinephrine-combined lidocaine for dental use is subacid (pH 4.6) which causes the pain. In this case, by neutralizing with bicarbonate(NaHCO₃), the start of acting is quick and the pain is reduced.
6. Reduce the injection frequency by using a long-acting anesthetic (bupivacaine).
7. Administer such as sedatives in prior to perform anesthesia.
Toxicity
1. Allergy.
2. Overdose.
a. Lidocaine 4.5mg/kg; Total dose 300mg, 15mL at maximum in a person weighing 60kg.
b. Epinephrine-combined lidocaine 7mg/kg; Total dose 500mg, 25mL at maximum in a person weighing 60kg.
c. When toxicity is suspected, administer oxygen immediately and make the patient to have hyperventilation.
When toxicity is suspected due to excessive absorption of prilocaine (EMLA®) treat the patient with methylene blue.
Insufficient Anesthesia
1. When the volume of anesthetic agent exceeds the maximum safe dosage as its local infiltration is required too much, reduce the dosage using the nerve block or using tumescent method that dilutes the anesthetic agent to lower concentration.
2. Use the anesthetic agent neutralized with sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO₃).
3. Since any infected tissue is difficult to anesthetize sufficiently, perform the procedures after treating the infection with anti-biotics except particular cases.
Prior Knowledge required for Prevention of Infections before and after the Surgery of Skin tumors
Normal flora of patient – The primary cause for infection of surgical wounds, advantages and disadvantages by disinfectant
1. Alcohol.
a. Act through contact. b. No washing capacity.
c. Inflammability d. The duration of action is not so long.
2. Chlorhexidine.
a. The start of action is quickened when use this combined with alcohol.
b. Cautions for use around the eyes.
c. The action is sustained even after wiping it off.
3. Povidone-Iodine.
a. Quick start of action.
b. The action is not sustained after wiping it off.
4. Hair: Cut but not shave.
Medical Staff for the Surgery
1. Hand washing, nail trimming.
2. Requires to take cautions for preparing any surgery-related hazards at all time.
Tools and Environment
• Clindamycin inside excised legion: Effective for preventing the wound infection and for reducing antibiotic-resistant risks.
• When Pseudomonas the common infectious bacteria in the ear wound is suspected, the quinolone antibacterials are effective .
• As the breakout of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is increasing in the community, the culture should be performed for every infection case.
• With or without purulent discharge, any pain, edema and erythema gradually increasing can be the characteristics of wound infection, therefore, the wound should be checked at intervals of 1 day, 3 days and 7 days so that any infection should be treated in early stage.
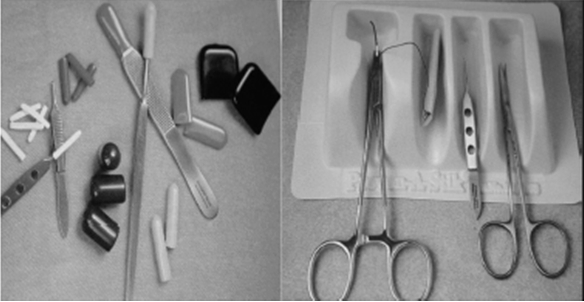
Figure 1 & 2. Prepare the surgical tool set by usage -Use a tray for preparation in advance.
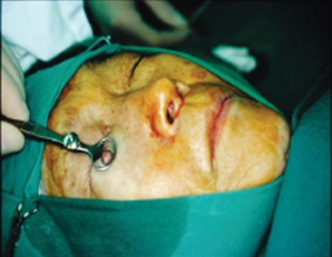
Figure 3. Prepare the right tool set by surgical region.
- To be continued -
▶ Previous Artlcle : #6. Treatment of Ingrown Toenail
▶ Next Artlcle : #8. Pre-Surgical Knowledge Part II for Preparation of Facial Tumorectomy in the Out-Patient





















