▶ Previous Artlcle : #3-1. B vitamins acting on the nervous, cardiovascular and hematopoietic systems
Vitamin B9 (Folic Acid)
Vitamin B9 (folic acid), also called folic acid, folate, and vitamin M, is known to be a vitamin that is important in the development of fetal nerves and blood vessels.
It is one of the homocysteine-lowering vitamins (B6, B9, and B12) (Figure 3).
Folate or folic acid deficiency tends to occur along with vitamin B12 deficiency.
HELIOSⅡ/LOTUSⅡ/HYPERION – Manufacturer: LASEROPTEK(www.laseroptek.com)
It causes glossitis as a symptom and is also related to malformations such as megaloblastic anemia, meural tube defects, spina bifida, and cleft palate.
The estimated average requirement (EAR) of folate (folic acid) in adult males and females is 320㎍ DFE/day, and the recommended intake (RI) is 400㎍ DFE/day, 120% of the EAR.
During the gestation period, the requirement of folate increases due to enlarged uterus, increasing blood supply, developing placenta, fetal growth, etc.
Basically, folate is recommended to be taken over the duration from 1 to 3 months before the start of pregnancy until at least the first trimester of pregnancy (13 weeks) or sometimes up to 1 month after parturition.
In usual cases, approximately 200㎍ DFE/day is added to the RI for the intake. Even during breast-feeding, 150㎍ DFE/day is added to the RI.
*Reference)
1ug DFE (Dietary Folate Equivalent)
= folate 1ug in food
= folate 0.6ug in nutritional supplement
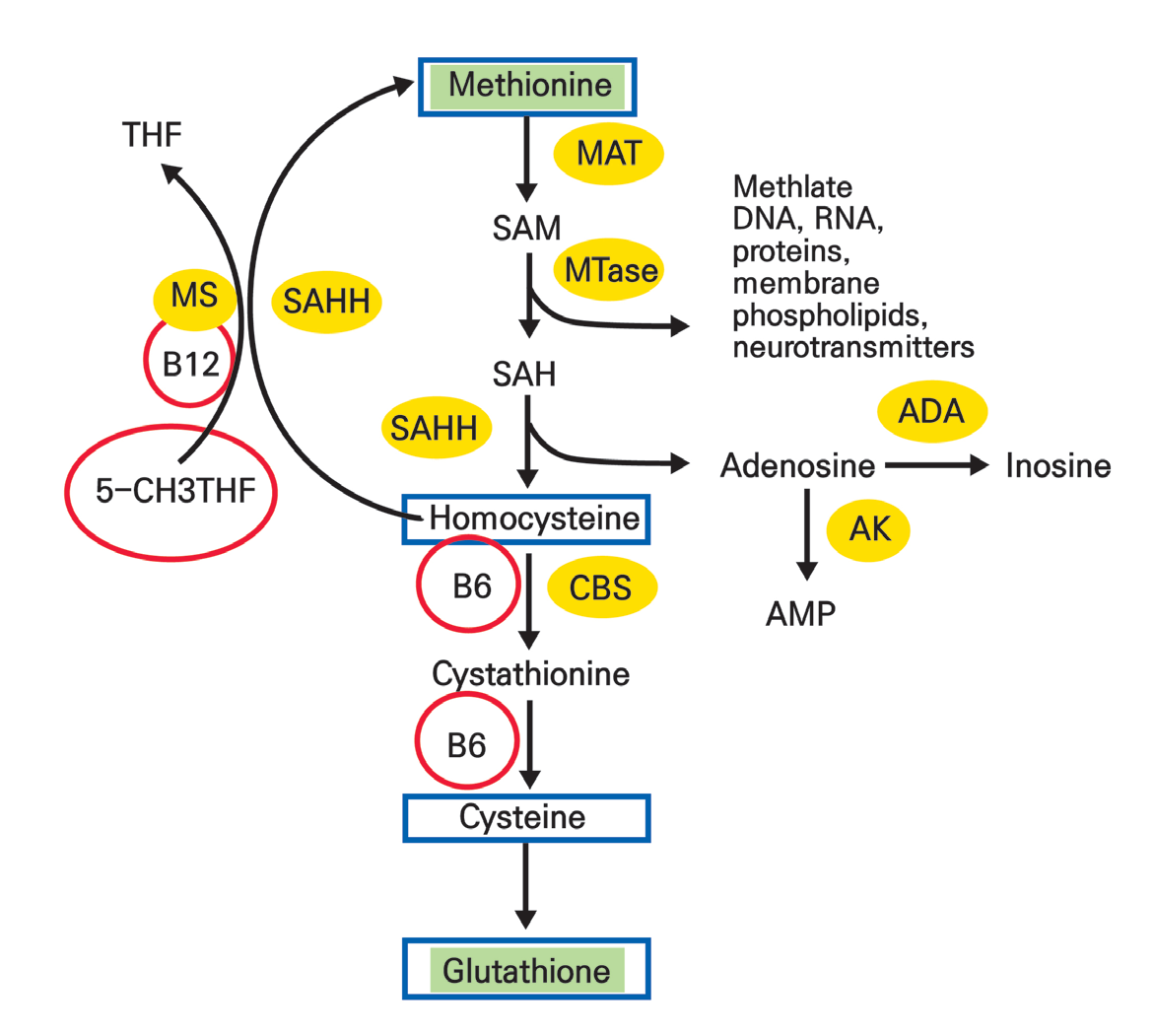
Figure 2. Homocysteine reduction pathway.
-To be continued