.jpg)
Toxic proteins compromised of heavy chain and light chain in electrophoresis and non-toxic proteins comprised of hemagglutinin protein (HP) and non-hemagglutinin protein (NHP). Most commercially available botulinum toxin is a complex type containing these two proteins. Xeomin has removed the non-toxic proteins, HP and NHP, and is comprised purely of toxic proteins of heavy and light chains. This is thought to give Xeomin the lowest risk of secondary tolerance. However, HP and NHP dissolve in the body after injection and does not impact antibody development and there are reports that only toxic proteins cause clinically significant neutralizing antibodies.
The purity of toxic proteins may play an important role in the risk of secondary tolerance. Recent research and development of botulinum toxin focuses on minimizing protein content and the related risk of secondary tolerance.
In clinical practice, I advise avoiding short intervals between treatments and using minimal doses to reduce the risk of secondary tolerance and treatment failure. It is important to only use minimal doses even in retouching procedures.
[Advertisement] Reandnè Thread Series – Manufacturer: GTG KOREA(www.gtgkorea.co.kr)
Cosmetic Application (Hyperfunctional Lines)
Forehead wrinkles
Forehead wrinkles form from lifting the eyebrows in surprise or fear. They also form from frequent, forced lifting of the eyebrows in ptosis. Some patients habitually look up while talking and have deeper forehead lines.
Over a long period of time, dynamic lines become static, which means they are visible even when the face is expressionless. Deep wrinkles may appear like scars and even create a visible indentation that do not smooth out from stretching the skin. Botulinum toxin can be used to correct forehead wrinkles before they become deeper.
Forehead wrinkles generally form from the action of the frontalis muscle which lies immediately under the subcutaneous fat. Unlike procerus, corrugator & depressor supercilli, and orbicularis oculi muscles that attach to the eyebrow and pull it down, the frontalis muscle is the only one that lifts the eyebrows. Above the forehead, it connects to the galea aponeurotica and occipital muscle in the back and extends laterally to the superficial temporal fascia. The frontalis muscle descends to eyebrow area and overlaps with the glabellar complex. Therefore, it is advisable to inject the toxin in this area as well (Figure 1).
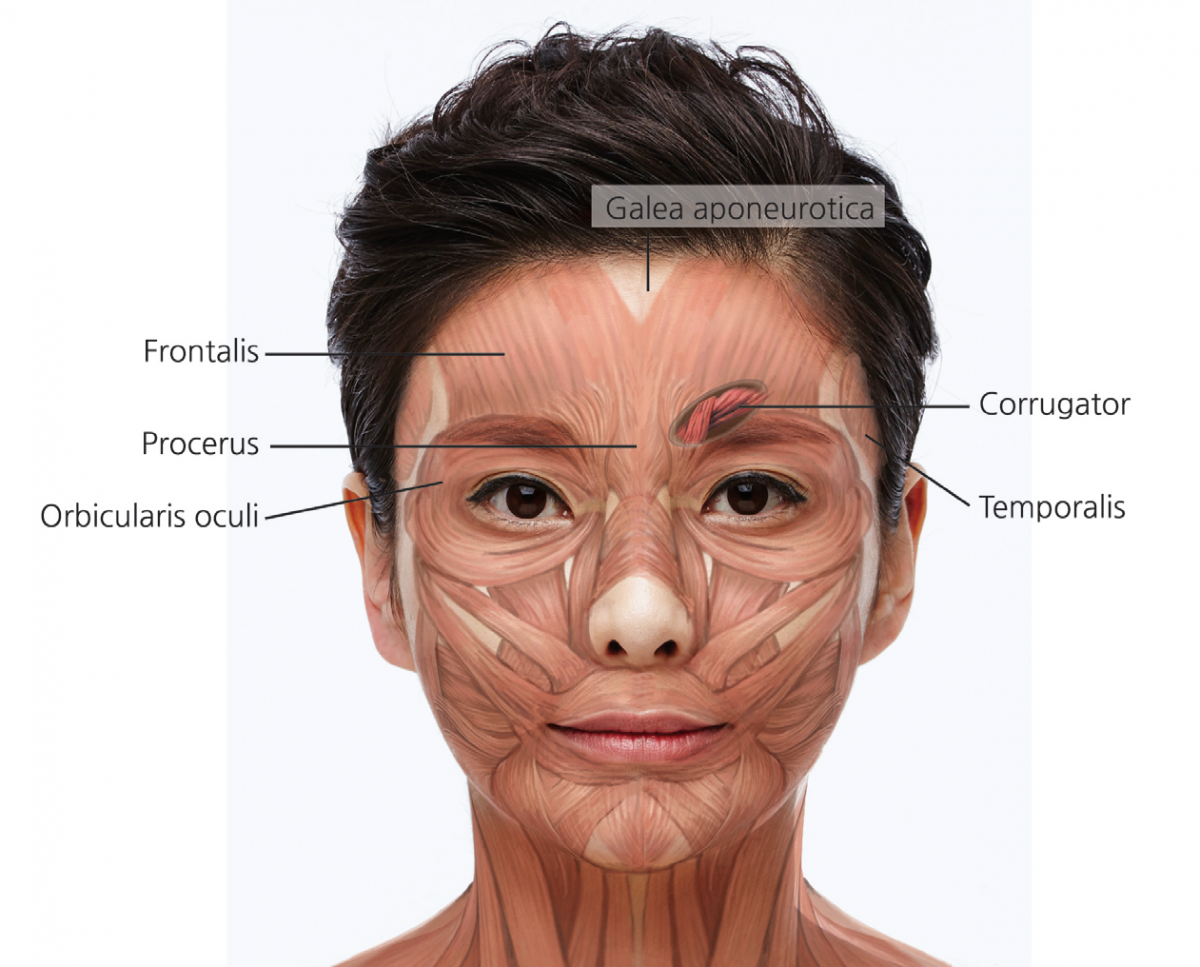
Figure 1. Facial muscles of upper face.
Paralyzing the vertical movements of the forehead muscles can cause an unnatural, frozen look. Moreover, many Asians have a weaker lift of the eyebrows compared to other races. The eyelid tissues and bone structure may also cause functional problems such as difficulty in opening the eyes or eyelid swelling. Therefore, instead of using deep, intramuscular injections over the extensive forehead area, I advise microinjection techniques where minimal doses are injected in differing depths depending on the site. This may help reduce the risk of functional problems and allow a more natural facial expression after treatment while bringing effective wrinkle removal.
There are two types to the forehead muscle; the type that bifurcates at the midline about 3.5cm above the superior orbital rim and the type that ascends all the way up to the hairline without bifurcation. The bifurcating type tends to have a gap where it starts to split and some say this area does not need injection. However, the muscle may bifurcate further up than this spot and some scholars recommend small-dose injection in this area as muscle still can be present in histological examination (Figure 2).
-To be continued




















