▶ Previous Artlcle: #10-2. Q-switched Ruby Laser
Side effects and treatment methods of Ruby Laser
The most typical side effects of Ruby Laser are hyperpigmentation and hypopigmentation.
To mitigate these side effects, it is important to determine pigmented lesions accurately and apply correct parameters that suit patient's condition. And the laser must be delivered stably to the tissue without changes in the output. Along with that, the beam quality is important.
Side effects may occur, as described above, in most cases if the beam is distorted or uneven in quality and high and low energies are present within the same spot.
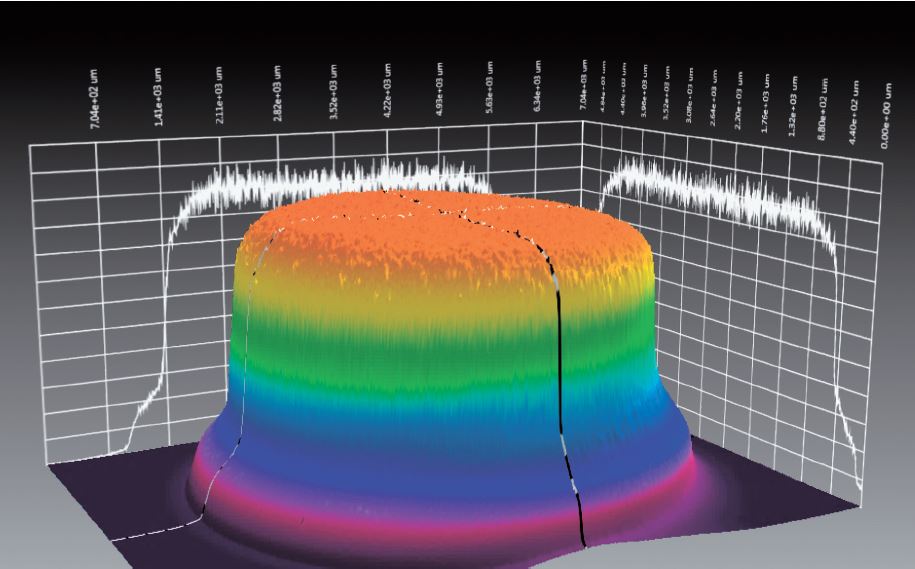
Therefore, it is important to select a device that provides uniform beam quality in the form of flat top(<Figure 3>) when Q-switched Ruby Laser is selected.
[Advertisement] Reandnè Thread Series – Manufacturer: GTG KOREA(www.gtgkorea.co.kr)
The indications of Ruby Laser include tattoos(black, blue, azure, brown, green), ABNOM, Ota nevus, Ito nevus, lentigo, café au lait spot, freckle, melasma, etc.
However, the treatment of benign tumor lesions, such as junctional nevus, congenital melanocytic nevus, and seborrheic keratosis, is ineffective due to thickness of lesions and therefore such conditions cannot be considered to be the indications.
Crust is always formed after the Ruby Laser procedure, and pigmentation may occur subsequently as a side effect.
Therefore, follow-up treatment with home care is important for minimizing the occurrence of side effects and for ensuring rapid improvement.
Figure. 3. Flat top beam mode.
-To be continued