▶ Previous Artlcle: #11-6. Ablative Fractional Laser
Lasers are used for a variety of purposes, such as pigmentation and vascular treatments, waxing, skin lesion removal, skin elasticity improvement, lifting, skin regeneration, sterilization and fat dissolution.
In particular, laser resurfacing using CO2 or Er:YAG laser has long been used for total rejuvenation in the area of skin cosmetology.
Laser resurfacing is a procedure that removes skin tissues including skin lesions and scars located in epidermis and on the outer layer of dermis by ablating skin ranging from epidermis to papillary dermis and through appropriate post-operative cares to help skin regeneration.
It is a very effective treatment; however, it can bring about several side effects such as skin redness, scars, sensitive skins and pigmentation, along with a longer recovery time after treatment.
[Advertisement] Reandnè Thread Series – Manufacturer: GTG KOREA(www.gtgkorea.co.kr)
Fractional Photothermolysis
In 2004, D. Manstein and R. R. Anderson RR explained the concept of fractional photothermolysis in the thesis titled "Fractional Photothermolysis: A New Concept for Cutaneous Remodeling Using Microscopic Patterns of Thermal Injury" published in Lasers in Surgery and Medicine.
In addition, they suggested that this procedure is a safe and effective method for skin regeneration because it regenerates tissues after a shorter recovery time without side effects, and as a result, shows improvement in the wrinkles of the photoaged skin.
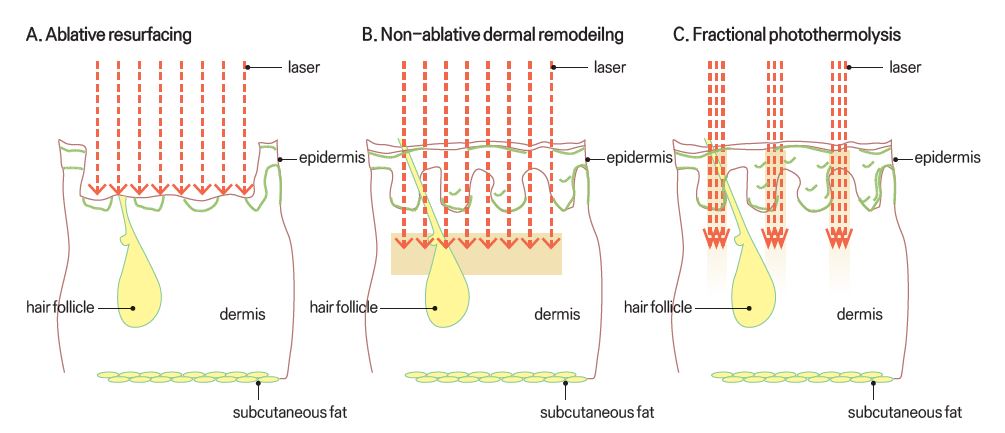
Figure 1. Conceptual comparison of ablative skin resurfacing(ASR), non-ablative dermal remodeling(NDR), and fractional photothermolysis(FP). A: ASR removes the epidermis and causes residual thermal damage within the dermis. Reepithelialization is delayed because of relative long migratory path lengths for keratinocytes that repopulate from skin appendages. B: NDR creates a layer of thermal damage below the surface without causing epidermal removal or damage. C: FP is the distribution of microscopically small volumes of thermal damage, MTZ, within the skin. Epidermal repair is fast due to small wounds and short migratory paths for keratinocytes.
-To be continued