▶ Previous Artlcle: #8-3. Er:YAG Laser
However, if milium, papulopustular acne, herpes simplex, contact dermatitis, microbism, etc. occurs, drug therapy and sedation are required to treat them, depending on individual condition.
The most problematic complications include prolonged erythema, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, delayed hypopigmentation, hypertrophic scar, and atrophic scar. Erythema or hyperpigmentation mostly improve naturally over time, but hypopigmentation or scar needs additional therapy because a natural recovery is difficult to be expected.
When it comes to hypopigmentation, it is highly likely to occur when lesions in the body are removed. Therefore, it is advised to inform patients that there may be onset of hypopigmentation prior to procedure, in order to prevent the possibility that a special problem related to this may arise.
[Advertisement] Reandnè Thread Series – Manufacturer: GTG KOREA(www.gtgkorea.co.kr)
If hypopigmentation appears as expected, it can be improved using Er:YAG fractional laser and 1550nm Er:Glass fractional laser. Persistent erythema can be quickly improved through the Genesis technique using pulsed dye laser, 1550 nm Er:Glass fractional laser, and long pulsed Nd:YAG laser.
As for hypertrophic scar, it can also be improved as its status is observed. If rapid improvement is desired, a single injection of triamcinolone (1:10) is effective. Atrophic scar can be improved through combination of various treatments involving fractional laser, TCA dot peeling, filler injection, air-fluid dissection, and subcision.
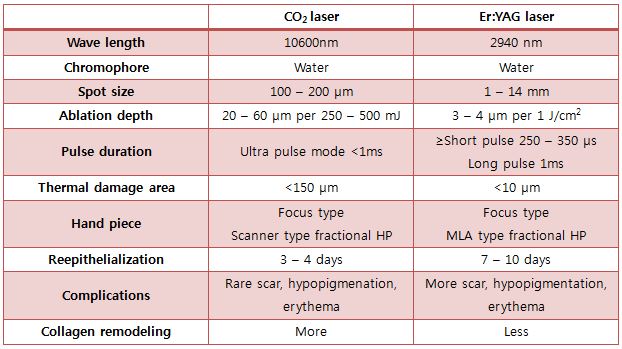
Figure 1. Comparison between CO2 laser and Er:YAG laser.
CO2 laser and Er:YAG laser can be compared as shown in the table below, but it does not mean that either of the two has absolute advantages over the other. In order to obtain favorable outcomes and reduce recovery period, it is indicated to engage in combined procedures by making the most of each other's advantages and making up for each other's disadvantages.
- To be continued