II. Mesh skin graft
Mesh skin graft is a type of split-thickness skin graft(STSG) with the main objective of covering a large skin defect with a small skin patch(Fig 1). Ratios of 1:1 and 1:2 are generally used but for larger coverage areas, ratios of 1:4 or even 1:9 are also used. In such cases, a cultured epithelial autograft or cultured epithelial homograft are used or human allograft is used to provide temporary coverage over the mesh skin in a sandwich technique. This can accelerate epithelialization between wide gaps in the mesh to reduce treatment time(Fig 2).
[Advertisement] ATLAS(Long pulse 532nm & 940nm dual wavelength) – Manufacturer: MEDRO(www.medro.net)
Mesh skin graft allows evacuation of blood, plasma as well as drainage of exudate through the holes and reduces likelihood of hematoma, seroma that inhibits graft survival. It has the benefits of high successful engraftment and quick and effective coverage of extensive areas. However, severe contracture may follow engraftment and cobble stone shaped scarring poses serious aesthetical problems. Therefore, mesh skin graft is not recommended in high-activity areas of the joint, as well as the face, neck, dorsum of the hand, and calves, etc. that are exposed.
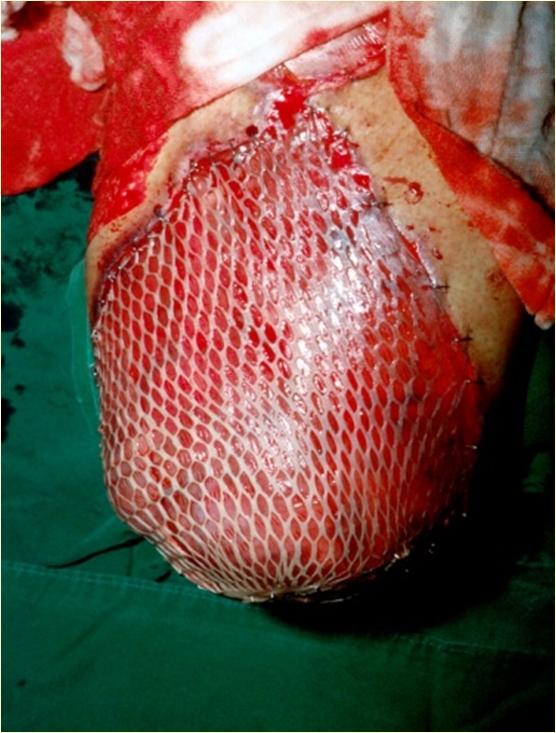
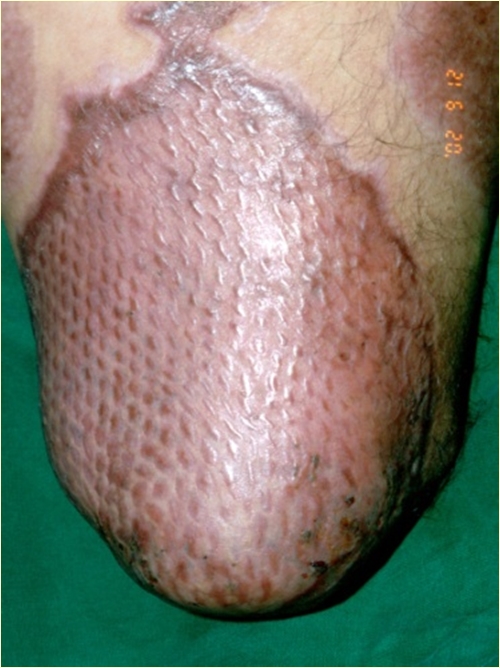
Fig 1. The cobble stone appearance 4 months after 1:3 mesh skin graft which compromises aesthetic outcome.
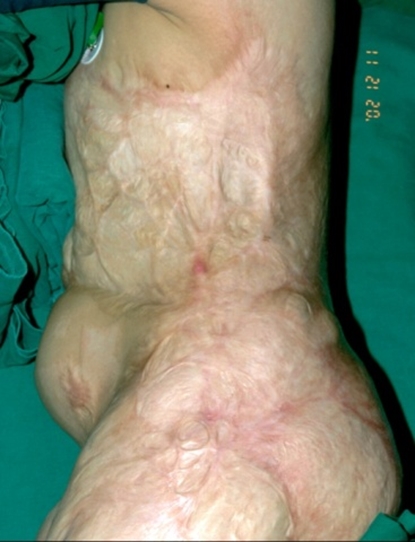
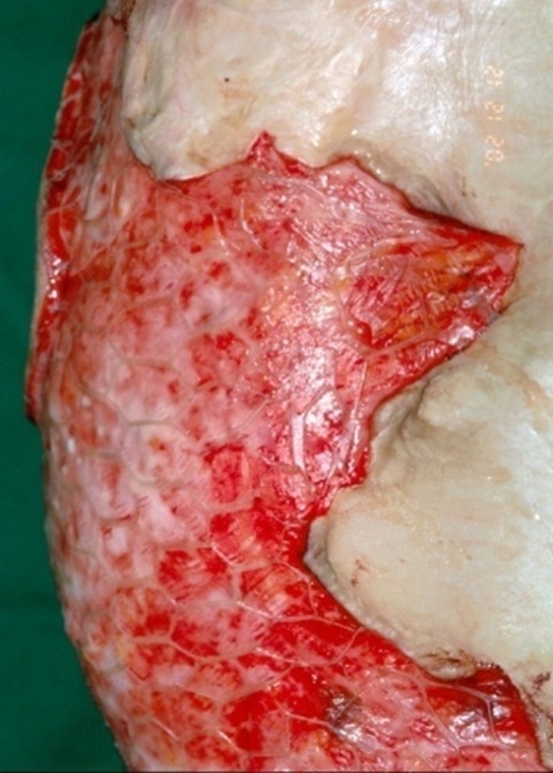
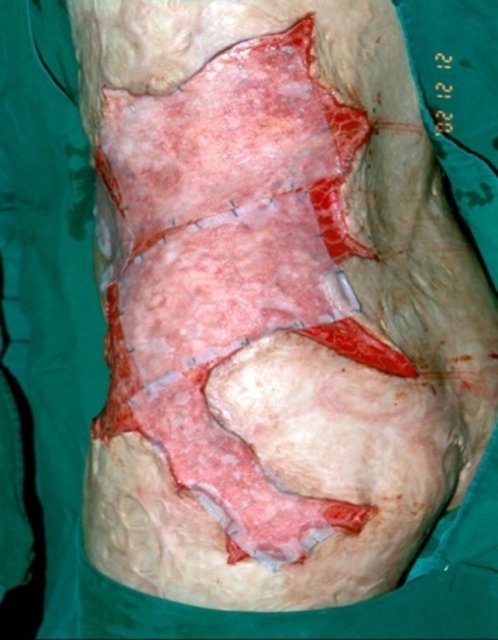
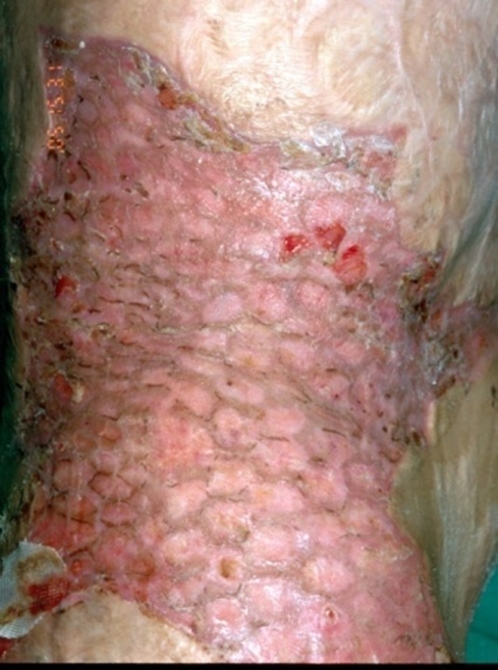
Fig 2. A 10-year-old boy. For reconstruction of severe scar contracture in the chest and abdomen due to flame burns in 70% of the entire body surface, dermal substitute AlloDerm and 1:6 auto mesh skin graft were performed. To increase graft survival and accelerate recovery, cultured epithelial autograft(CEA) was simultaneously performed. By 19 days after the procedure, the dermal substitute and CEA had been engrafted and most of the wound had healed.
-To be continued-