
In this article, we will take a look at procedures in the temple area. The temple area is an important anchoring point for thread lift procedures of the face but is often forgotten in volume enhancing procedures. Doctors often underestimate the value of the temple area to the aesthetics of the entire face. The temple area is clearly visible when the patient wears her hair in a ponytail or a head band. The temple refers to the facial area of the temporal fossa, where the temporalis muscle is located. This area can be concave from birth or becomes indented due to age-related atrophy of soft tissues. The hollowness of the temple area can make an Asian face appear more aged as Asians tend to have a more pronounced cheek bones. A more youthful face can be achieved by providing volume to the temple area that connects smoothly with the forehead, profile of the face, and outline of the cheekbones. A young face has a smooth and rounded outlines of the forehead and upper face.
Anatomical structure of the temple
Complicated nerve and vascular structures exist in the temple area and accurate understanding of anatomy is critical for success of treatment. The temporal muscle lies in the temporal fossa. On the surface of this muscle, lie two layers of fascia. The superficial temporal fascia (STF) or temporalparietal fascia (TPF) surround the superficial temporal artery and vein, which lie under the skin of the temple area, and connect to the SMAS. The deep temporal fascia or temporalis muscle fascia lie in the deeper layers. The two layers of fascia touch on the zygomatic arch, around which exist some fat and middle temporal veins. The middle temporal vein passes about 20mm superior to the zygomatic arch. This vein is about 5-10mm thick and is drained through the superficial temporal vein. Incorrect injection of the dermal filler can cause pulmonary embolism and great deal of caution is needed in this area. The sentinel vein is another one to watch out for. It is about 2~3mm thick and tends to be pronounced when excess amount of filler is used. This vein is connected to the cavernous sinus and caution is advised to avoid serious complications in this area.
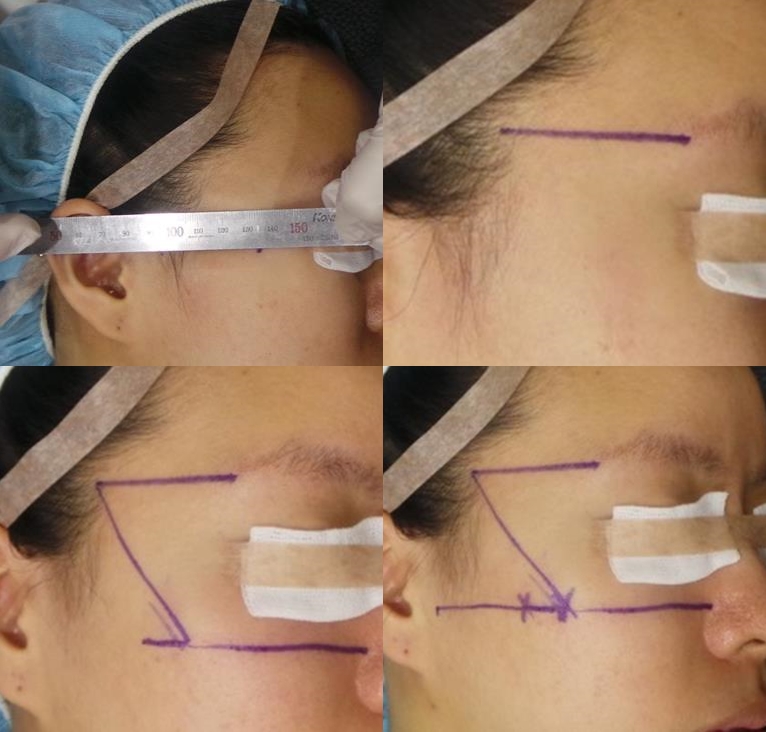
Figure 1. Have the patient in a sitting position, pull the possible external entry points with fingers to predict the outcome. Draw a line connecting to eye area and make a marking for a 6 cm cog thread. Use a ruler.
[Advertisement] Ultra Skin/Pastelle – Manufacturer: WONTECH(www.wtlaser.com)
-To be continued




















