
Tattoos are permanent markings on the skin. As the word “permanent” suggests, tattoo ink remains in the dermis causing indelible pigment change. This also means, the ink will remain as long as the skin containing it. What makes tattoos permanent? And why do tattoos often fade or even disappear completely? It is necessary to understand the ink used in tattoo procedures in order to understand all phenomena associated with tattoo. I’d like to examine tattoo ink closely over two articles.
In this article, we will discuss basic ingredients and properties of conventional tattoo ink. The next article will focus on new tattoo ink products that have improved upon the conventional options. Through these articles, you will learn about ingredients of tattoo ink which has over 5,000 years of history and how they behave in the human body.
Tattoo Ink Ingredients
Tattoo ink consists largely of two main ingredients; pigment for color expression and a carrier that effectively delivers and evenly distributes the pigment in the skin. Various minerals and carbon black have been used as pigment ingredients for a long time. Currently, iron oxides are the most commonly used mineral and pigments are added to it to create various colors(Table 1).
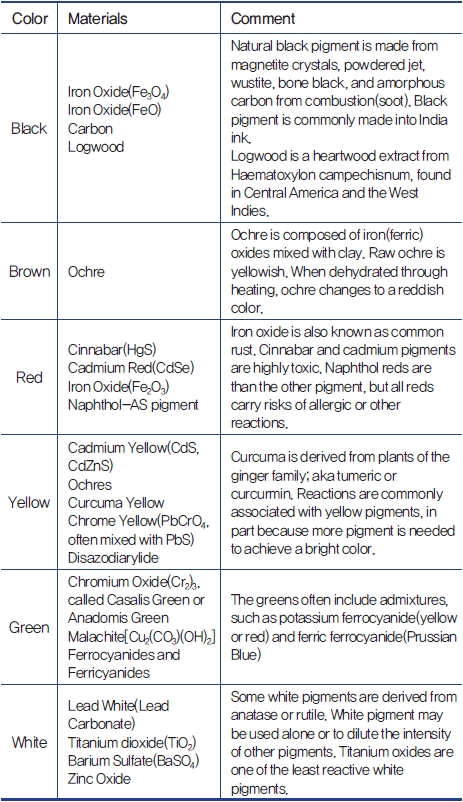
Table 1. Composition of Tattoo Pigments.
Iron oxides is a chemical compound composed of iron and oxygen and naturally exists in the forms of iron oxides (FeO), ferric oxide (Fe2O3), and triiron tetraoxide (Fe3O4), etc. Through chemical processing that adjusts natural ore and moisture content, it can take on various colors including black, yellow, red, brown and purple, etc. Processed iron oxides is used as an abrasive for jewelry making, magnetic tape, or semi-conductor component. When used as a food coloring, it is categorized as E172. In medicine, it is used as a contrast agent in diagnostic imaging as well as a radioactive tracer in tumor diagnosis.
[Advertisement] Reandnè Thread Series – Manufacturer: GTG KOREA(www.gtgkorea.com)
As shown in Table 1, pigments, a main ingredient of tattoo ink, can be divided into original mineral pigments, modern industrial organic pigments, vegetable-based pigments, and plastic-based pigments. Most of allergic reactions, scars, phototoxic reaction, and other ink-related complications are caused by pigments. In particular, plastic-based pigments have vivid color expression and may cause side effects that are just as strong as their colors. Simply put, the brighter and more vivid the color, the more harm to the skin.
-To be continued




















