
1. Use of thyroid hormone therapy
In 1874, Dr. William W. Gull first reported of hypothyroidism and in 1891, it was discovered that the extract of sheep thyroid gland can be used to improve hypothyroidism as well as myxedema simultaneously, which had the added benefit of weight loss. Many people tried to attribute obesity to hypothyroidism and thyroid hormone drugs were used to treat obesity. However, hypothyroidism-related obesity is less common. Thyroid hormone therapy stopped being used as anti-obesity medication due to a serious side effect of causing thyroid disorder in people with normal thyroid.
2. The nightmare of 2,4-Dinitrophenol(2,4-DNP)
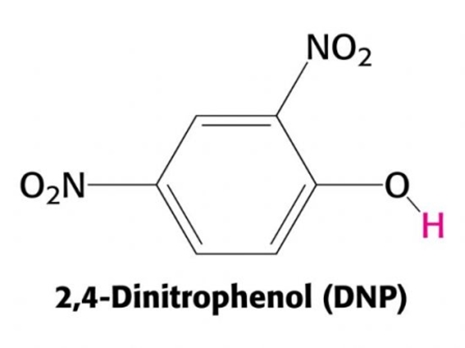
Image 1. Chemical formula of HOC6H3(NO2)2.
<Image 1> shows the chemical formula of HOC6H3(NO2)2 an organic compound widely used in the 1930s as a dieting aid. It is an organic compound with a sweet mustard flavor and was used as a food dye in the early days. With the industrial revolution, mass production of food began and the yellow dye was used in bread to give the impression of higher egg content. It was discovered that the workers in the food plant using 2,4-DNP kept losing a lot of weight. Cutting and Tainter of Stanford University reported 2,4-DNP drastically increased the metabolic rate, leading to a widespread use of this substance as a dieting aid. In the first year of its sales, over 100,000 people used it in the US.
Looking only at weight loss, 2,4-DNP can be said to be one of the most effective. Unlike most anti-obesity drugs that focus on curbing the appetite, this drug significantly increases the body’s energy consumption and brings weight loss regardless of food intake. 2,4-DNP causes uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation. In simpler terms, it causes inefficient production of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) in the mitochondria and consumes the produced ATP through heat generation. Therefore, the body burns stored fat to compensate for energy deficiency, leading to weight loss.
However, 2,4-DNP was highly toxic, causing serious and acute side effects including vomiting, high fever, sweating, headache, and cardiovascular problems. Long-term exposure resulted in cataract, fatal damage to the cardiovascular and central nervous systems. Overdosing could lead to death from extreme fever. After the first case of death was reported in 1918, approximately 67 cases of death were reported and 2,4-DNP was banned in the mid 1930s.
Image 2. Alvogen`s anti-obesity drugs.
[Advertisement] A-One LITE(Facial Diagnosys System) – Manufacturer: BOMTECH(www.bomtech.net)
-To be continued-




















