
Hur Hoon, M.D., Ph.D.
Choice Dermatology Clinic, Pyeongchon, Korea
.jpg)
Figure1.A solitarycafé au lait spot on the right buccalarea(before treatment:10/19/2012).
.jpg)
Figure2.A complete clearance of café au laitspot(after treatment with Golden Parameter:12/19/2012).
.jpg)
Figure3. There is no recurrence at 18 months follow-up(6/5/2014).
.jpg)
Figure4.Partial unilateral lentiginosis on the left periorbital area and left maxillary area(before treatment).
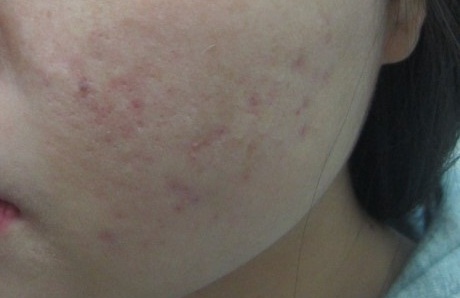
Figure5.A complete clearance of partial unilateral lentiginosis(after treatment with Golden Parameter).
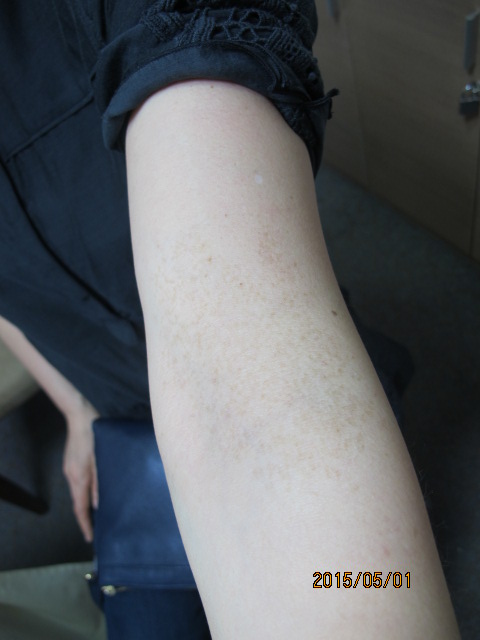
Figure6.Partial unilateral lentiginosis on the left antecubital area(before treatment).
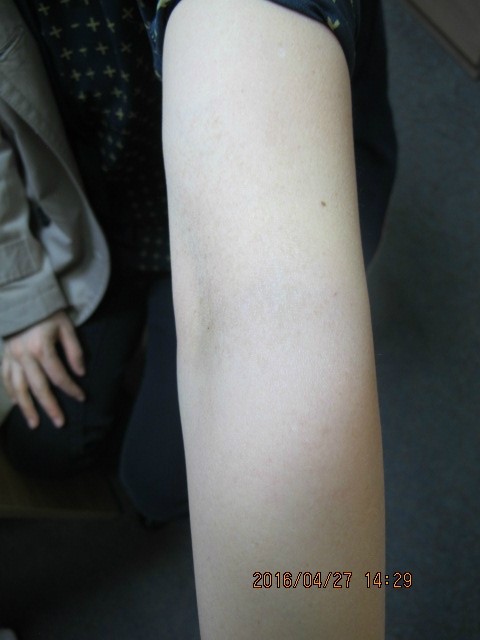
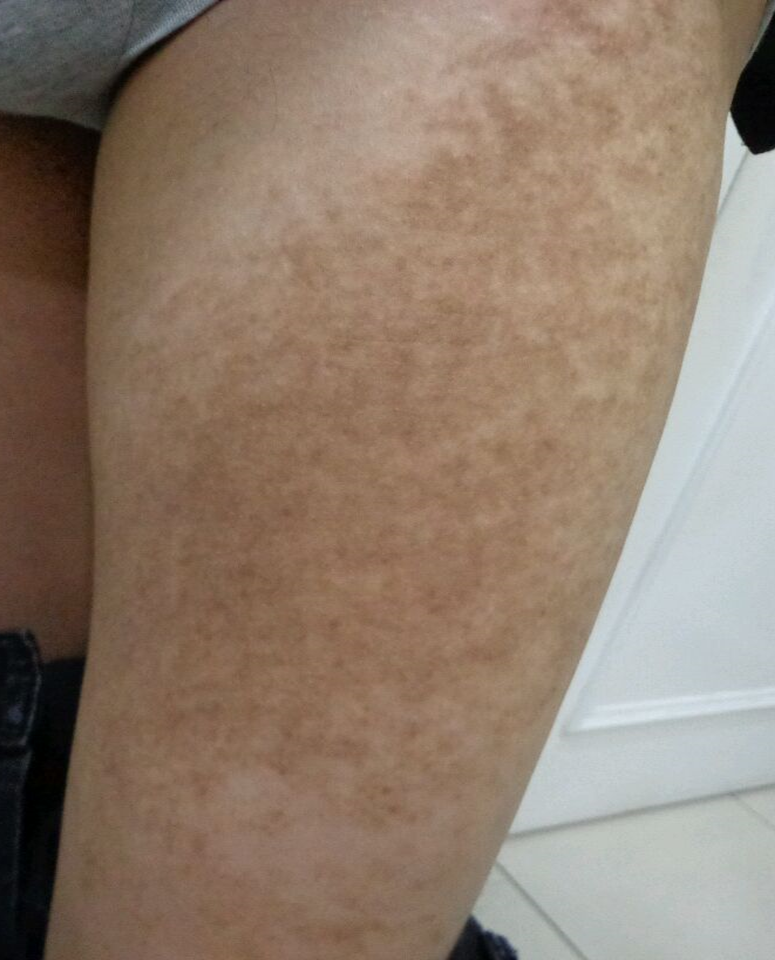
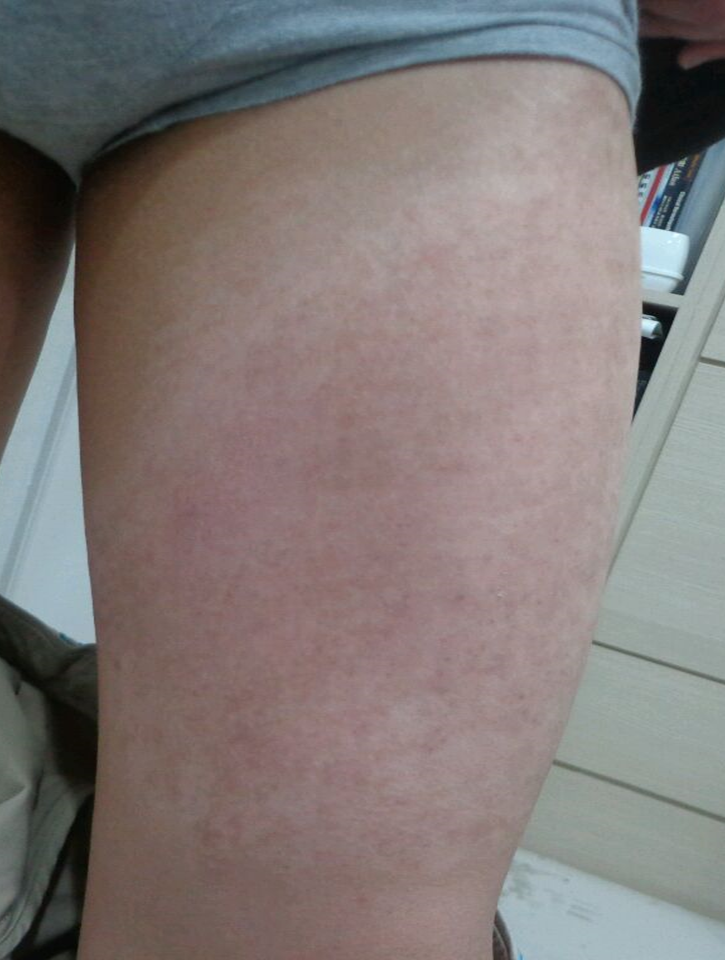
Figure8.Becker’s nevus on the left thigh(before treatment).
[Advertisement] FCR® (Fractional Prickle CoralCalcium Regentron) – Manufacturer: (www.illglobal.com)]
1.Nguyen JT, Yan AC, James WD. Large solitary cafe au lait spots. A report of 5 cases and review of the literature.Cutis. 2004;73:311-3116.
2.Landau M, Krafchik B. The diagnostic value of cafe au lait macules. J Am Acad of Dermatol.1999;40:877-890.
3.Pique E, Aguilar A, Farina MC et al. Partial unilateral lentiginosis:report of seven cases and review of the literature. Clinic and Experi Dermatol.1995;20:319-322
4.Grande SH, Harris R, Hansen CD et al. Androgen receptor expression patterns in Becker’snevi: An immunohistochemical study.JAmAcadof Dermatol.2008;59:834-838
5.Hur H. The treatment of café au lait spot using Dr. HurHoon’s Golden Parameter Therapy.J Dermatol and Ther.2016;1:1-4
6.Anderson RR, Margolis RJ, Watanabe S et al.Selectivephotothermolysis of cutaneous pigmentation by Q-switched Nd:YAGLaser pulses at 1064,532 and 355nm. J Invest Dermatol.1989;93:28-32.
7.Geronnemus RG. Q-switched ruby Laser: therapy of nevus of Ota. Arch Dermatol. 1992;128:1618-1622
8..Mihara M. Eczematous dermatitis occurring on cafe au lait spot after Laser radiation. Case RepDermatol. 2013;5:133-137.
9.Schepper SD, Boucneau J, Haeghen YV et al. Cafe au lait spots in neurofibromatosis type 1and in healthy control individuals: hyperpigmentation of a different kind? Arch Dermatol Res.2006;297:439-449.
10.Hattori H, Kawashima M, Ichikawa Y et al. The epidermal stem cell factor is over-expressedin lentigosenilis:Implication for the mechanism of hyperpigmentation. J Invest Dermatol.2004;122:1256-1265.
11.Okazaki M, Yoshimura K, Suzuki Y et al. The mechanism of epidermal hyperpigmentation incafe au lait macules of neurofibromatosis type 1 may be associated with dermal fibroblast-derived stem cell factor and hepatocyte growth factor. Bri J Dermatol. 2003;148:689-697.
12.Okazaki M, Youshimura K, Uchida G et al. Epidermal hyperpigmentation in non-syndromicsolitary cafe au lait macules may be associated with increased secreation of endothelin-1by lesional keratinocytes. J Plastic Sur & hand Sur. 2005;39:213-217.
-The End-
Hur Hoon, M.D., Ph.D.
Choice Dermatology Clinic, Pyeongchon, Korea




















