▶ Previous Artlcle : #9-2. Donor Harvesting Technique: FUS(S) VS. FUE
There are three types of graft placement.
The first is to create holes with a surgical scalpel or a syringe in advance and transplant the follicles to the holes with tweezers. The second is to create holes with a syringe and transplant the follicles simultaneously. The third is to use a hair transplanter. A majority of doctors in Korea prefer the last one.
[Advertisement] ATLAS(Long pulse 532nm & 940nm dual wavelength) – Manufacturer: MEDRO(www.medro.net)
In US, the first method is most commonly used; a doctor creates holes and then a technician transplants hairs. On the other hand, hair transplanter is used for most cases in Korea, which should be performed by doctors only.
Scalps are harvested from the back of the head together with about 1 cm of hair because it is easier to hold hair than follicle to insert the hair follicle into the needle of the hair transplanter, with less damage to the hair follicle.
It is also useful for counting the number of hair follicles and for detecting transplanted areas, so as not to leave empty areas.
I personally take much attention to the following issues when conducting hair transplantation using a transplanter:
❶ Direction of transplanter during the course of transplantation
❷ Transplanter angle during the course of transplantation
❸ Transplantation depth and transplanter needle length
❹ Creating a hairline
❺ Density gradient by areas
1. Direction of Hair Follicles
As hair grows in a radial pattern as shown in <Fig. 1>, placing the transplanter in the direction as shown in <Fig. 1> can guarantee natural growth of the transplanted hair. Hair may look volumeless and flat if the patient has very fine hair. If this patient parts the hair on the left and comb over to the right, the transplanter can be placed toward the left to volumize the hair (Fig. 3).
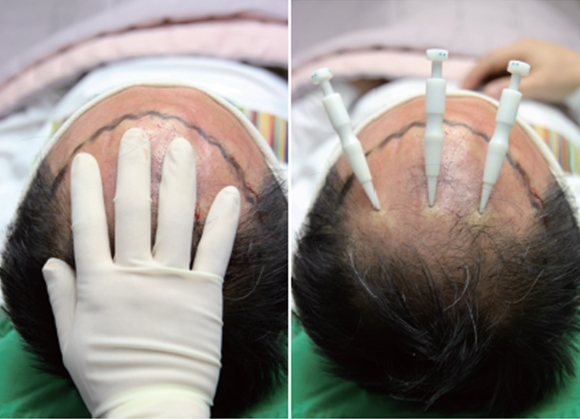
Fig. 1. The direction of fingers corresponds to the direction of normal hair growth.
Fig. 2. Appropriate direction of the transplanter.
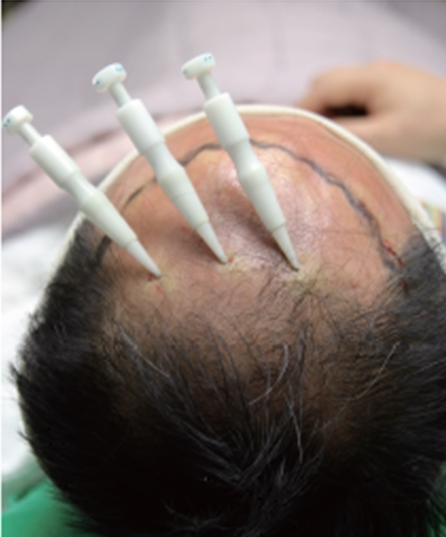
Fig. 3. Placing the transplanter to the one direction may volumize the hair in patients with fine strands of hair.
2. Angle of Transplanter
The exit angle of normal hair varies according to areas, but is generally 60-70 degrees at the forehead and at the top of the head. Although each operator may have a different opinion, I prefer to maintain the entry angle of the transplanter at 60-70 degrees, if possible.
Transplantation at an angle of 90 degrees or above may deepen the depth of the transplanted follicle, possibly causing folliculitis or pitting. The direction of the transplanted hairs may seem unnatural as well (Fig. 4).
In general, the scalp does not curve a lot from the top to the middle of the forehead, but the angle along the borderline of the forehead varies a lot between individuals, calling for much attention on angle adjustment (Fig. 5).
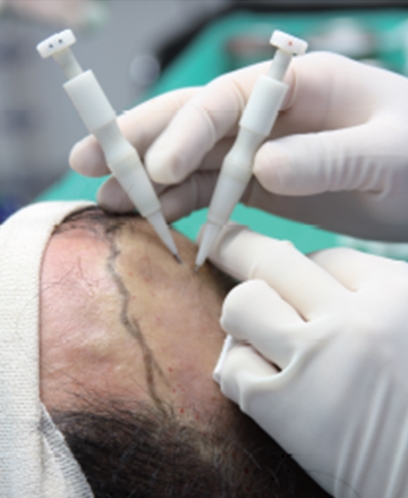
Fig. 4. Transplanter on the left – appropriate angle; Transplanter on the right – inappropriate angle.
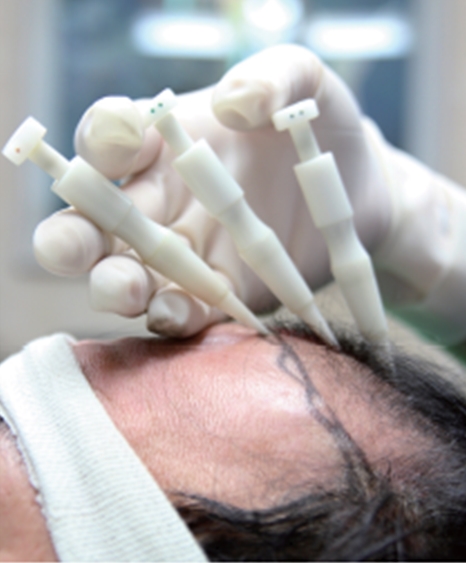
Fig. 5. The angle of the transplanter should be well adjusted depending on the variable curbs of the scalp according to areas. The borderline of the hairline particularly needs a special attention.
-To be continued-
▶ Next Artlcle : #10-2. Hair Transplantation using a Transplanter