Before conducting hair transplantation, patient’s medical history and medication history should be investigated and laboratory findings should be confirmed if there is any issue that may affect the surgical procedure. The followings should be prepared before hair transplantation:
[Advertisement] ▶ ULTRA THIN WALL NEEDLE – Manufacturer: AESPIO(www.aespio.com)
Preparations
1. Medication history should be investigated and any drug that may be associated with hemorrhage should be discontinued or switched to other drugs. Aspirin, among others, has irreversible effect on platelet which lasts for 7-10 days until the platelet dies. On the other hand, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which inhibits cyclooxygenase but has reversible effect on platelet, and ibuprofen, which has short half-life, can be discontinued for only 1 day. Other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can be discontinued for several days. Heavy drinkers need to stop drinking for about a week because they are susceptible to intraoperative bleeding due to reduced platelet function. Vitamin E and Vitamin B complex may induce bleeding susceptibility, which lasts for a about 3 weeks; Vitamin E and B complex should be discontinued for 2-3 weeks. Warfarin inhibits the synthesis of K-dependent clotting factors II, VII, IX and X, but does not seriously induce intraoperative bleeding susceptibility; epinephrine mixed with local anesthesia may reduce bleeding. Nicotine should be discontinued for several weeks before the operation because it reduces blood flow. However, when a long-term heavy smoker stops smoking for a short period of time, excessive intraoperative bleeding may occur due to vasodilatation.
2. Drugs that may have interaction with patient’s baseline drug: Monoamine oxydase inhibitors (tranylcypromine, isocarboxazid, nialamide) should be discontinued 1 week before the operation since it may cause fatal outcome when combined with lidocaine. Hypertensive patients have increased risk of intraoperative bleeding, thus they need to control their blood pressure by continuously taking antihypertensives until the operation. However, if a patient has been taking beta-blocker Propranole (inderal), it should be replaced to another drug, because it may be life-threatening when combined with epinephrine.
3. Antibiotics: Unlike general skin operations, prophylactic antibiotics for hair transplantation has not been established yet, but it is commonly used. When using antibiotics, 2 hours before the operation, rather than after the procedure, is preferred. Prophylactic antibiotics is advisable for patients with high risk of bacterial endocarditis. Other than that, it is advisable to shampoo the night before and on the morning of the operation.
4. Sedatives before and after the operation: Patients can be relieved by using diazepam or zolpidem.
5. Corticosteroid: Corticosteroid is commonly used to reduce facial edema. The effect may be different depending on the timing of administration, dose, type, and the patient’s characteristics. Prednisone and dexamethasone are commonly used; prednisone 60mg is orally administered or dexamethasone 8mg is injected intramuscularly on the morning of the operation. After than, prednisone 60mg is orally administered on the morning the day after the operation, and then the dose may be reduced to 30mg on the next day, and by 5mg every day afterward.
6. Laboratory findings: CBC, urinalysis, VDRL, Hepatitis B and C antigen and antibody and HIV infection are tested. Among others, communicable diseases, such as hepatitis B, hepatitis C and HIV, should be tested so as to protect both patients and medical staffs.
7. Preoperative hair length and styling: Donor site wound can be covered well if the hair length above the donor site is 4-6cm or longer. Recipient site also needs proper length of hair so that the wound could be covered. Permanent wave or dyeing is available from 2 weeks after the operation, but should be avoided until the scabs are fallen off after the operation.
8. Various forms including informed consent form: Patients should be informed of the operation method and expected outcomes before obtaining informed consent form from them. A checklist should be prepared to investigate preoperative medical history, medication history, allergic history and laboratory tests. Patients should be also provided with a handout that summarize the information that patients need to know before and after the operation.
9. Photographs: Photographs should be taken before the operation for postoperative evaluation of outcomes.
Anesthesia
The biggest concern among patients receiving hair transplantation would be postoperative outcome and perioperative pain. In my personal experience, most patients have fear of pain and everyone has different threshold for pain. If a patient experiences severe pain, he/she will have negative idea about postoperative treatment and about second or third operations. Thus, it is desirable to minimize the pain as much as possible.
The most commonly used local anesthesia for hair transplantation is injecting a mixture of lidocaine and epinephrine. Lidocaine exerts anesthetic effect in 2-4 minutes after injection, which lasts for 1-2 hours when used alone, or 2-4 hours when mixed with epinephrine (1:200,000). Lidocaine mixed with epinephrine is absorbed more slowly, increasing the stability of lidocaine.
The recommended dose is 7mg/kg (maximum 500mg) when mixed with epinephrine (1:200,000). For example, in an adult weighing 70kg, the maximum dose of 1% lidocaine, mixed with epinephrine (1:200,000), is 49ml, but greater doses have been used without particular side effects in various local anesthesia. When injecting a large dose, appropriate amount should be injected with some time intervals about 30 minutes.
Bupivacaine lasts for about 4 hours, or 8 hours when mixed with epinephrine. Anesthesia of longer duration is beneficial for perioperative as well as postoperative pain control.
1. Donor Site Anesthesia
For donor site anesthsia, ring block is performed using a mixture of lidocaine/bupivacaine and epinephrine. The anesthetic agents are injected at the level of dermis and subcutaneous fat, left and right at certain interval from 1cm below the donor site. Ring block anesthesia requires about 5-10 minutes to exert the effect. Tumescent anesthesia is often performed by injecting large amount of diluted lidocaine and epinephrine to the middle level of fat layer. This method is known to 1) facilitate the tissue collection by spreading the interval between the target follicle and blood vessels and nerves, 2) facilitates tissue resection by increasing the tissue strength of donor site, 3) reduces bleeding, and 4) reduces the total required amount of anesthetic agents. It may be uncomfortable, however, when using a transplanter because the hair shaft is easily separated from the surrounding tissue in the course of separating graft. Patient’s pulse rate and blood pressure may increase during donor site harvesting, due to the fear and anxiety from having to lie face down on the operating table. Patting on the patient’s back makes the patient relieved, inducing blood pressure reduction.
2. Recipient Site Anesthesia
Patients generally feel more pain during anesthesia on recipient site than on donor site, and this should be fully discussed with patients. Ice pack or vibrator may be used with anesthesia to reduce the pain from injecting anesthetic agents. Ring block is commonly used after blocking supraorbital nerve and supratrachlear nerve for local anesthesia of recipient site (Figure 1).
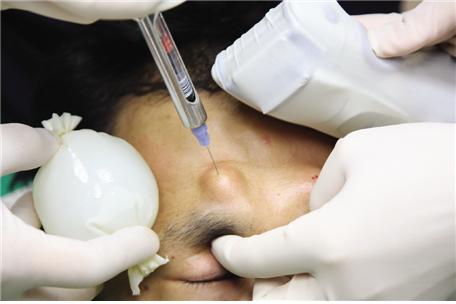
Figure 1. Recipient site anesthesia:Supraorbital nerve block·Ice pack or vibrator may be used with anesthesia to reduce the pain from injecting anesthetic agents.
Nerve block can be safely conducted by confirming supraorbital notch 2cm above the brow. 2% lidocaine 1.5-2ml is injected. As supraorbital nerve located at between the periosteum of the forehead bone and muscle moves to the skin surface, the needle should be inserted deep enough considering the thickness of the muscle, when performing nerve block. The needle itself may cause nerve damage, in the course of nerve block; acute stinging sensation or tingling sensation as if electrified means nerve was pricked, in which case the needle should be retreated immediately. Nerve block needs about 3-10 minutes to exert anesthetic effect. After the nerve block, ring block can be performed by injecting local anesthetic agents along the designed line, approximately 1cm before the operating line, to reduce pain. In order to reduce intraoperative bleeding susceptibility, field block is performed on the recipient site with anesthetic agents including epinephrine. It is safe to draw the piston back before injection to avoid intravascular injection. Care should be taken in this process, because the needle can be swayed back and forth or left and right, damaging the blood vessel and nerve. It is also recommended to feel the expansion of the tissue by placing a finger toward the end of the needle to confirm that the anesthetic agents are injected in the tissue. In addition, adding triamcinolone for field block can be helpful for reducing postoperative facial edema.
- To be continued -
▶ Previous Artlcle : #5. Complications after Hair Transplantation and the Prevention
▶ Next Artlcle : #7. Donor Harvesting Technique